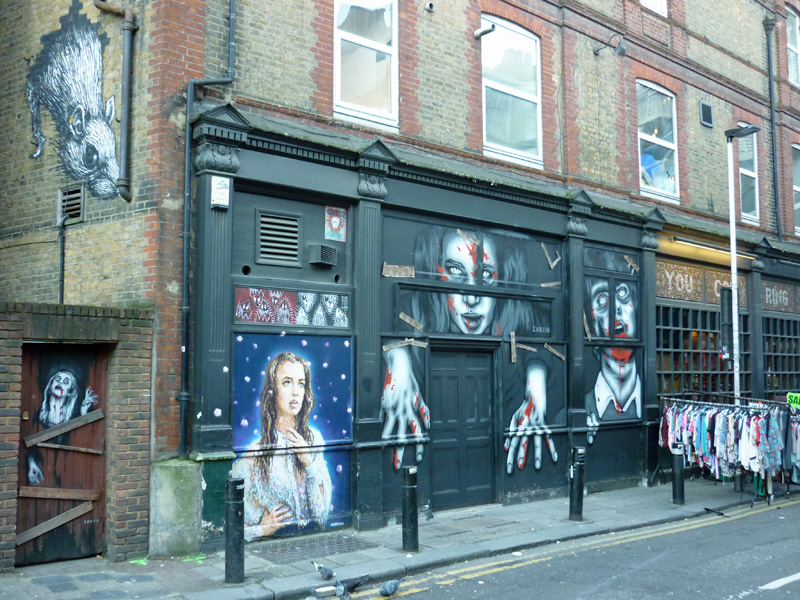
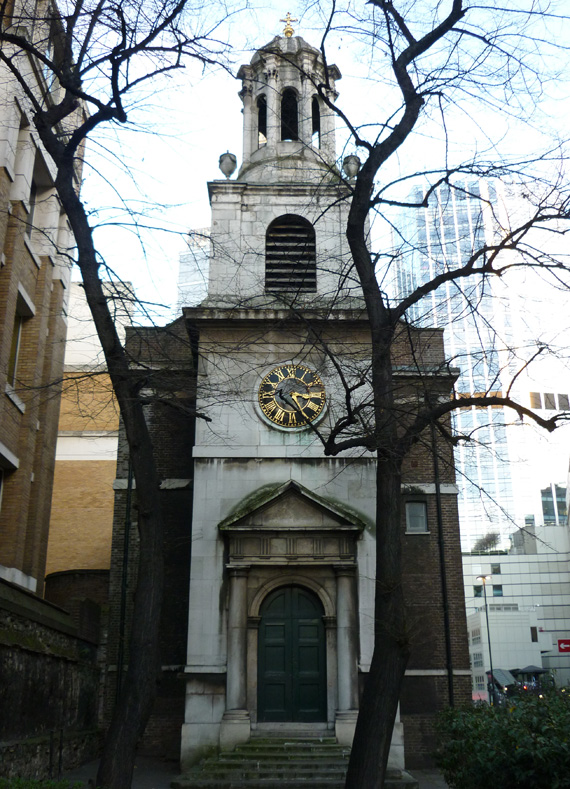
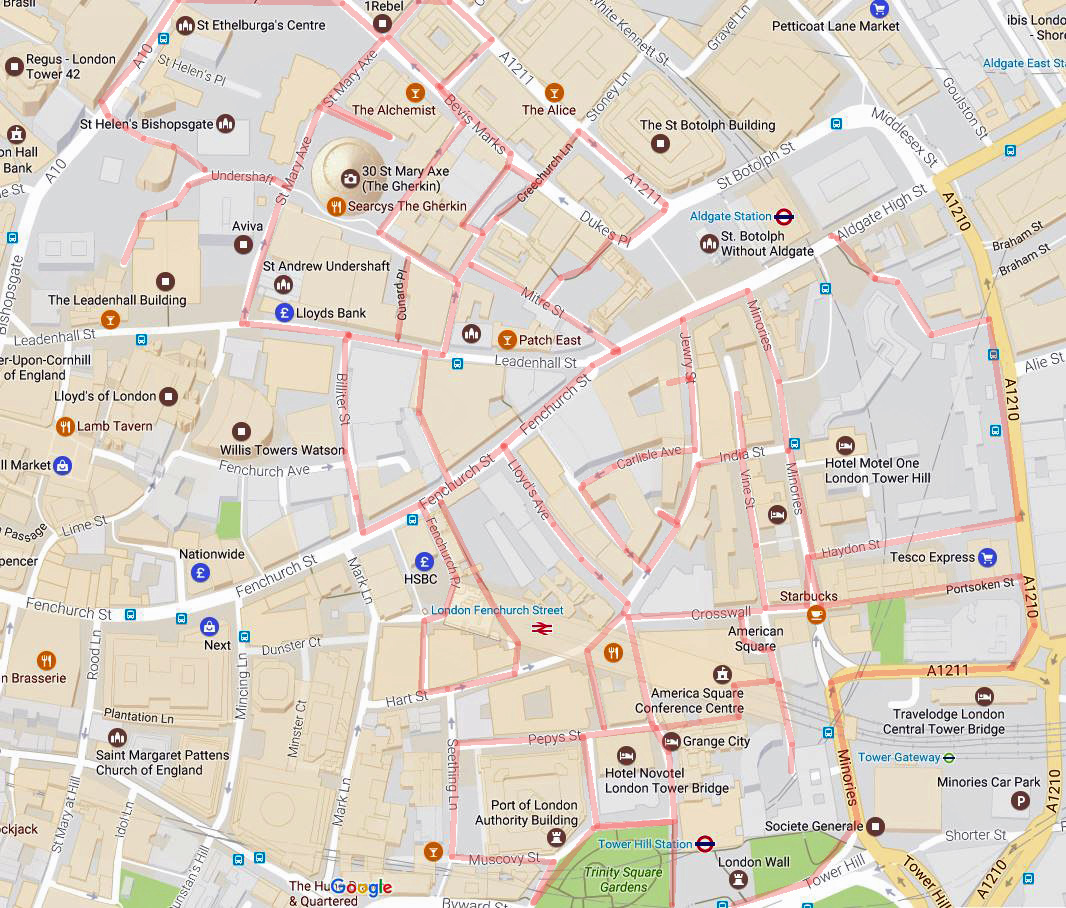
Continuing north from where we left off last time, but with a much less ambitious itinerary, today’s excursion sees us back in the East End. We’re visiting Aldgate East and Whitechapel, specifically the area bounded to the north by Commercial Road (A13) and to the south by Cable Street and stretching from Mansell Street to Cannon Street Road west to east.
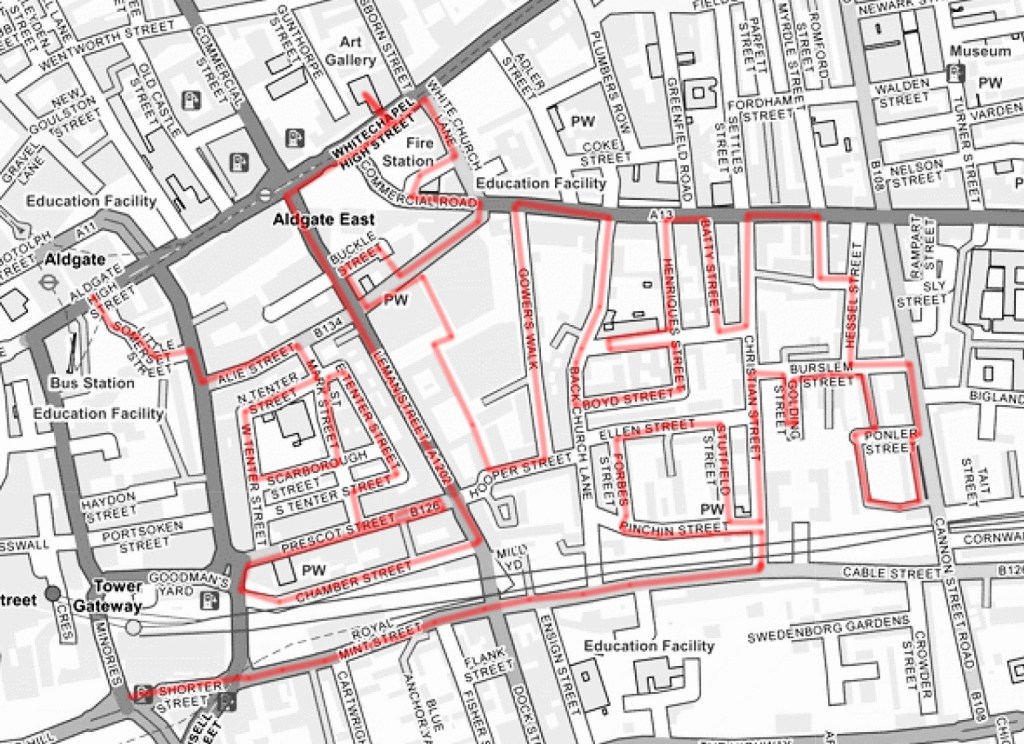
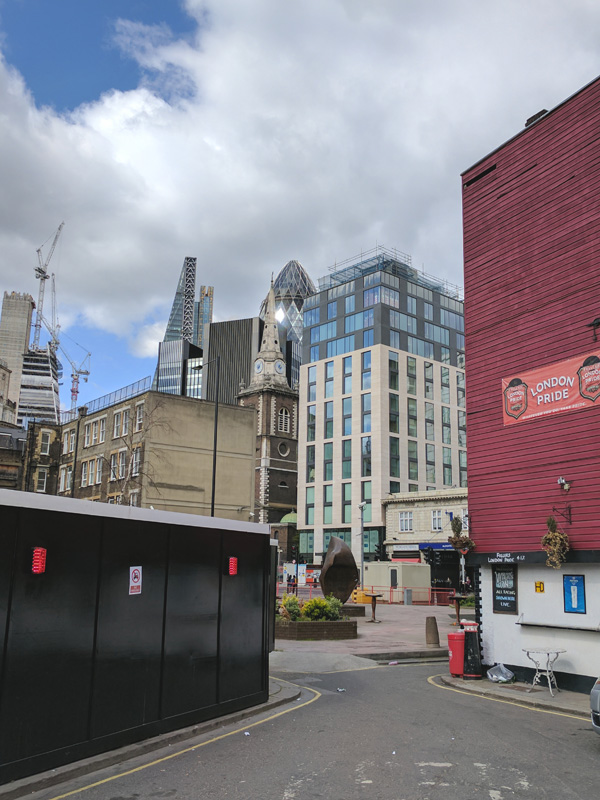
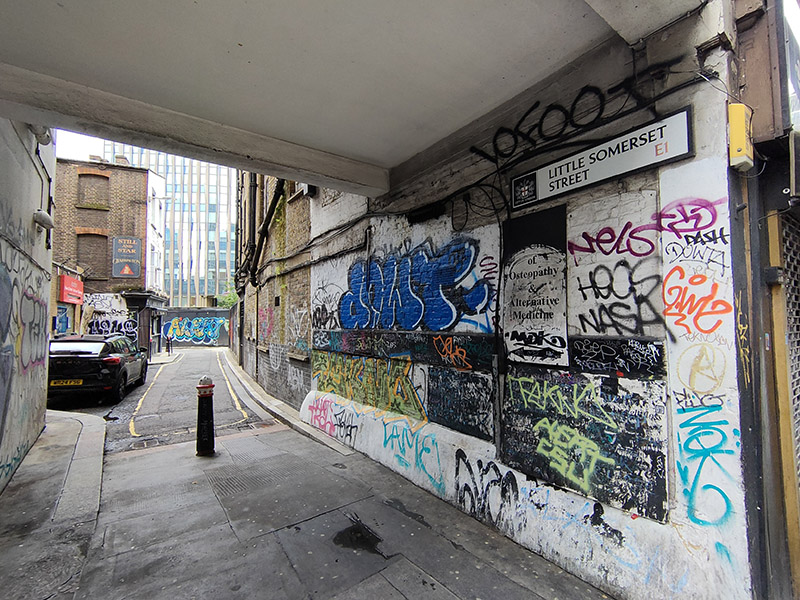
We start today’s journey at Aldgate tube station, crossing the road to cut through Little Somerset Street to Mansell Street, which replicates a very small part of the route we undertook on Day 20. This takes us past the Still and Star pub which at the time of that previous visit in 2017 was still a going concern. However, it was closed in 2020 and a application to demolish it and build an office development on the site was approved by the City of London (inside whose boundaries it just about lies). As you can see from the pictures below that development has yet to get underway; not unrelated to the pandemic I suspect. The loss of almost any pub is to be mourned but the demise of The Still and Star is especially sad as it was believed to be the sole example in the City of London of what is sometimes described as a ‘slum pub’ – in other words, a licensed premises converted from a private house. The name is also unique; apparently the pub originally had its own still, which was housed in the hayloft above, while ‘star’ refers to the Star of David, witnessing the Jewish population of Aldgate in the nineteenth century.
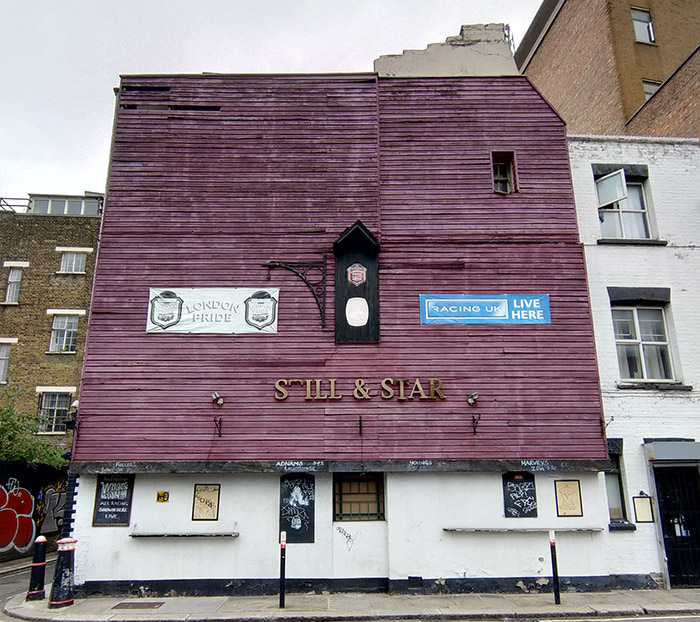


Mansell Street marks the actual boundary between the City of London and the borough of Tower Hamlets. Historically this was a pretty sharp dividing line but in recent years the office blocks and smart residential complexes have been encroaching beyond that line and starting to slightly change the tenor of an area that has for decades been home to a predominantly working class Bangladeshi community.
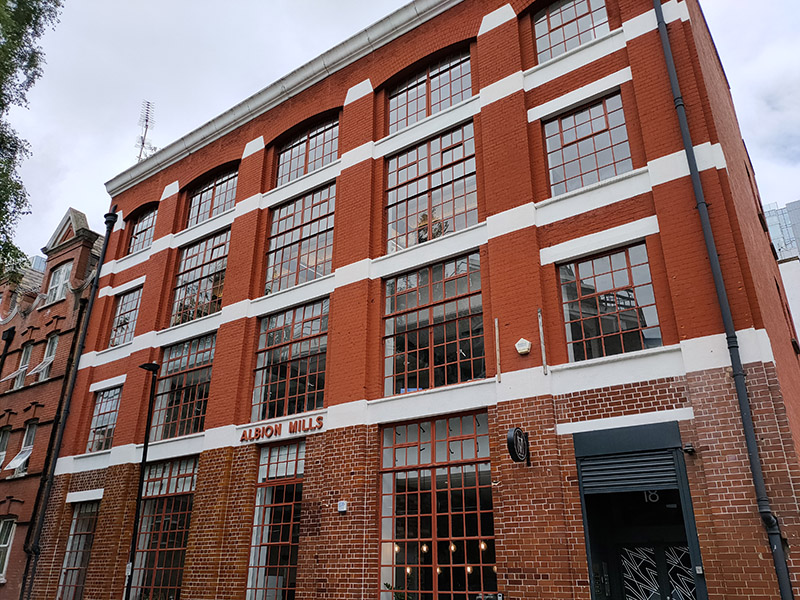
On the other side of Mansell Street we head east along Alie Street then turn right into a web of streets comprising Mark Street, North Tenter Street, West Tenter Street, East Tenter Street, South Tenter Street and Scarborough Street. The five-bay, four-storey, brick-faced warehouse at 18 East Tenter Street was built in 1905 for Israel Hyman and Sons, rag merchants. The architect was Gilbert Henry Lovegrove (1878–1951), a biographer of Sir John Vanbrugh, the builder S. Goodall of Stoke Newington. By the 1940s the building was being used as a ladies’ clothing factory called Albion Mills, a name that has been retained for its current incarnation as an office block.
We leave the various Tenter Streets behind via Mark Street onto Prescot Street, coming face to face with the erstwhile Whitechapel County Court, designed by Charles Reeves and Lewis G Butcher and built in 1858-9 in the then-popular Italianate style. Next door to this stands the Princess of Prussia Pub. The present building dates from 1913. Its predecessor, built in the mid 18th century, became a pub in the same year the County Court opened (and subsequently provided most of its trade) and was named in homage to the marriage of Princess Victoria (one of Queen Victoria’s daughters) to Frederick William, Crown Prince of Prussia one year earlier.
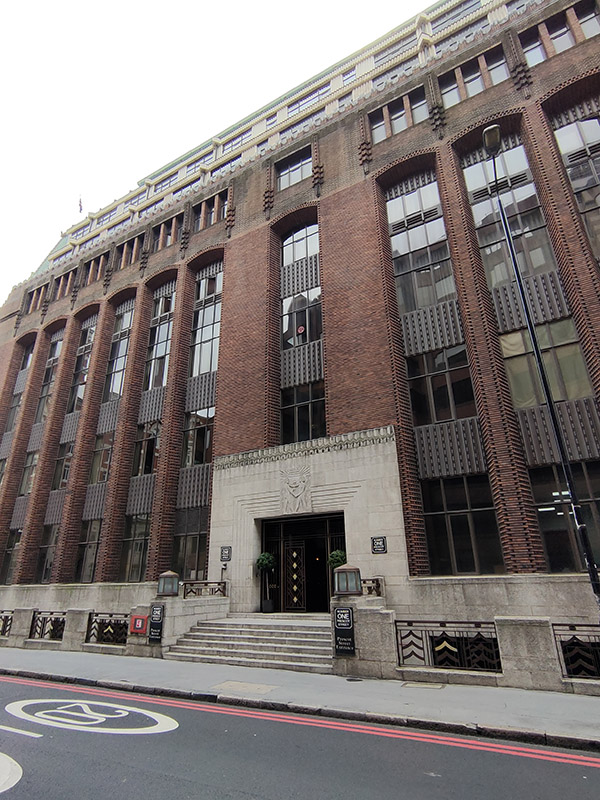
No. 1 Prescot Street is the imposing Grade II listed former Cooperative Wholesale Society building, once known as The Tea House. It was built between 1930 and 1933 to a design of architect, L G Ekins and is a rare example in Britain of the German Expressionist style of architecture. That rarity is hardly surprising in retrospect. Ironically, although this area suffered considerably in the Blitz, the Tea House survived intact.
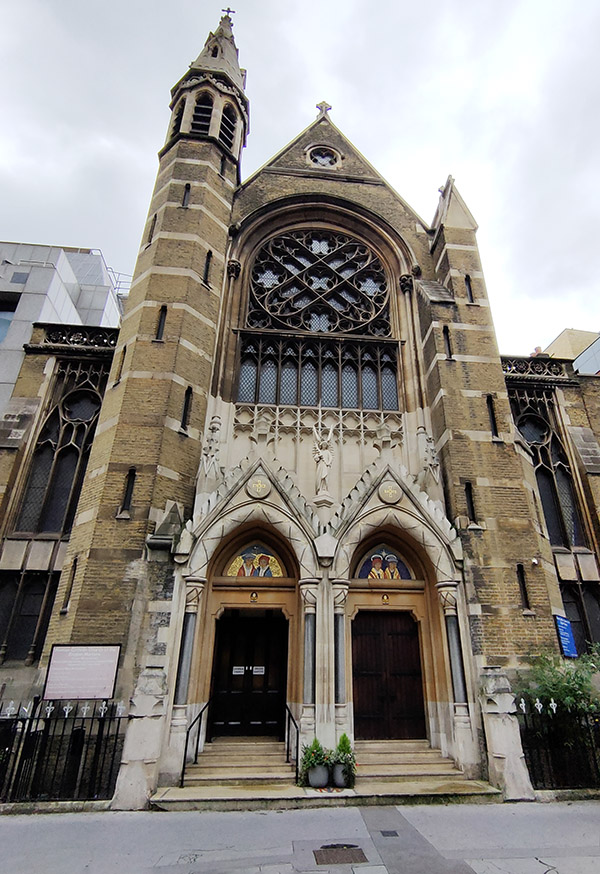
In the mid 1700s, Prescot Street was briefly home to the London Infirmary before it became the London Hospital (now the Royal London Hospital) and moved elsewhere in Whitechapel. The building, which no longer stands, was subsequently occupied by The Magdalen House for Reception of Penitent Prostitutes. An old alleyway, Magdalen Passage, in between the old County Court and the HQ of the Royal College of Psychiatrists, survives to commemorate the name. Further to the west at no.30 stands The Roman Catholic English Martyrs Church, designed by Edward Welby Pugin. The foundation stone was laid by the then Archbishop of Westminster, Cardinal Henry Manning in 1873.
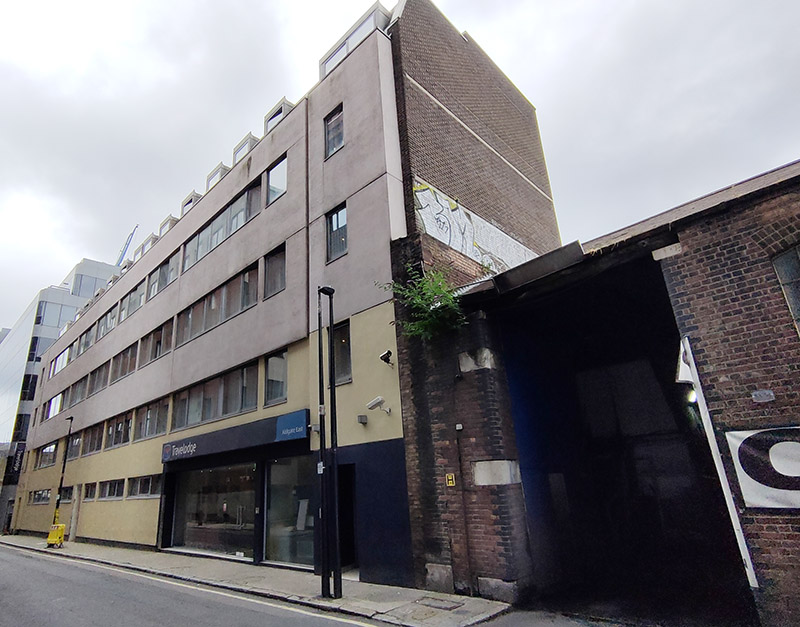
At the western end of Prescot Street we turn the corner and continue our eastward trajectory along Chamber Street which runs parallel to the DLR line and boasts, in the face of some stiff competition, the least inviting Travelodge I have yet to encounter (they’re so unproud of it it doesn’t even show up on Google maps).
At the end of Chamber Street we turn left onto Leman Street, named after Sir John Leman (1544 –1632) a merchant from Beccles (near Lowestoft) who served as Lord Mayor of London in 1616 and who used the proceeds from his trading in dairy products to purchase and build on this part of Aldgate.
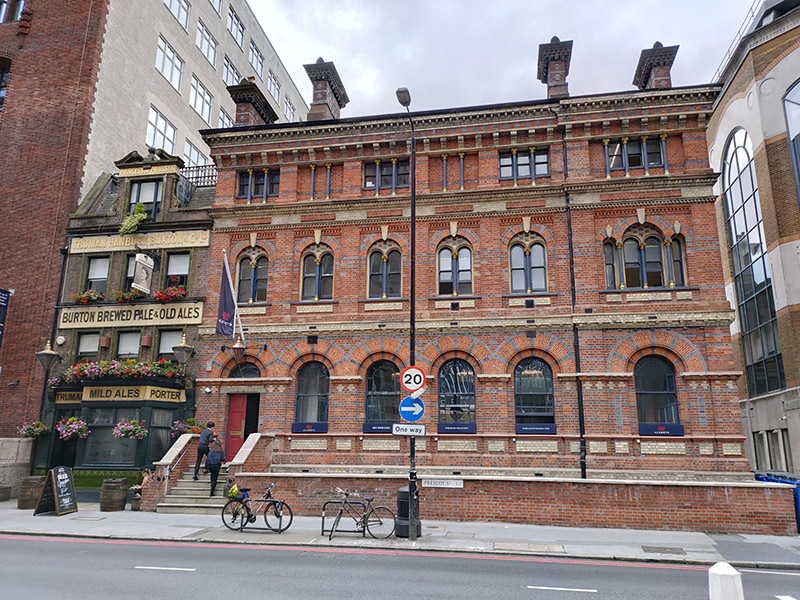
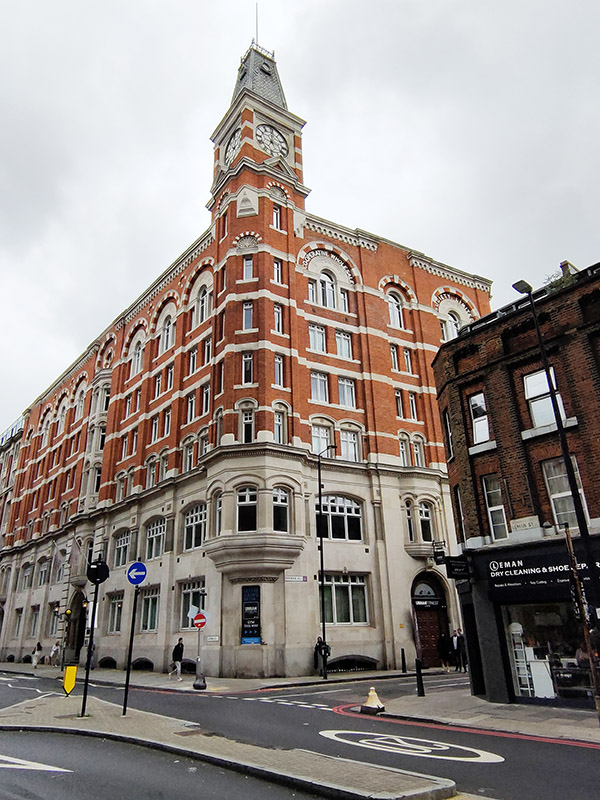
Prior to the construction of No.1 Prescot Street, the Cooperative Wholesale Society (what we now know as the Co-Op) had built an impressive London headquarters at 99 Leman Street in 1885-87. At the formal opening of the building, the CWS announced that it should “be their aim to make this beautiful building a common home for all the various movements having for their object the interest and advancement of the working people“. The building incorporated a sugar warehouse and so in time became known as Sugar House. In recent years it has been converted into luxury apartments which are listed at the kind of prices that would formerly have been unheard of in this area.
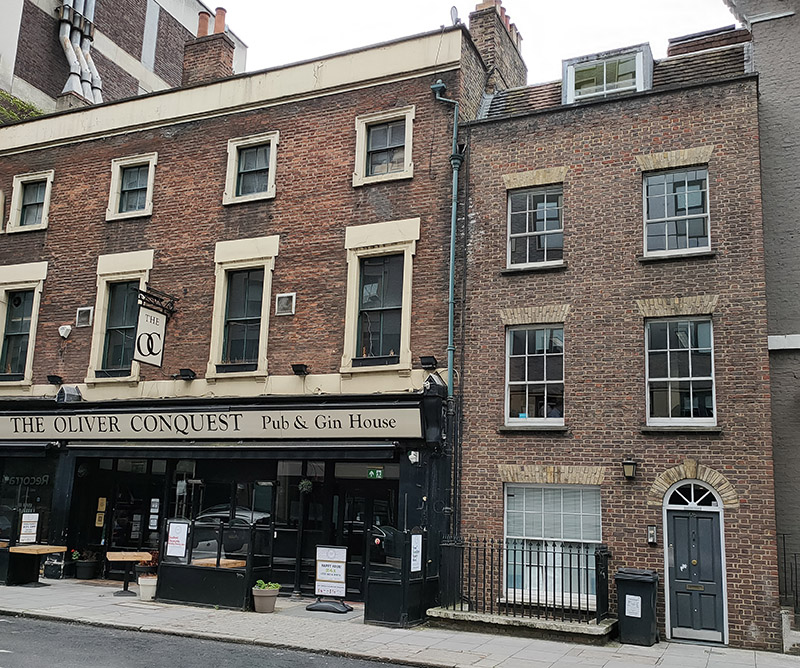
Further north on Leman Street is the Oliver Conquest pub. This dates from the mid 19th Century and was originally called the The Garrick as it was attached to the first Garrick Theatre, which was situated behind the pub. Benjamin Oliver Conquest was the theatre manager there in the early part of the 19th Century hence the name (nothing to do with Oliver Cromwell’s ravages of Ireland thankfully). This is another Grade II listing.
At the top of Leman Street we turn right onto Whitechapel High Street where we’re immediately confronted by another example of shameless association with the area’s most infamous character.
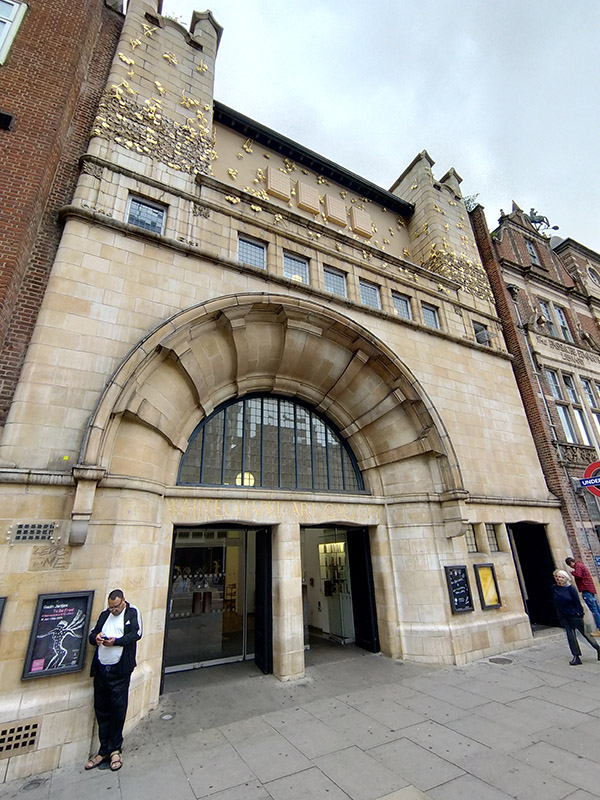
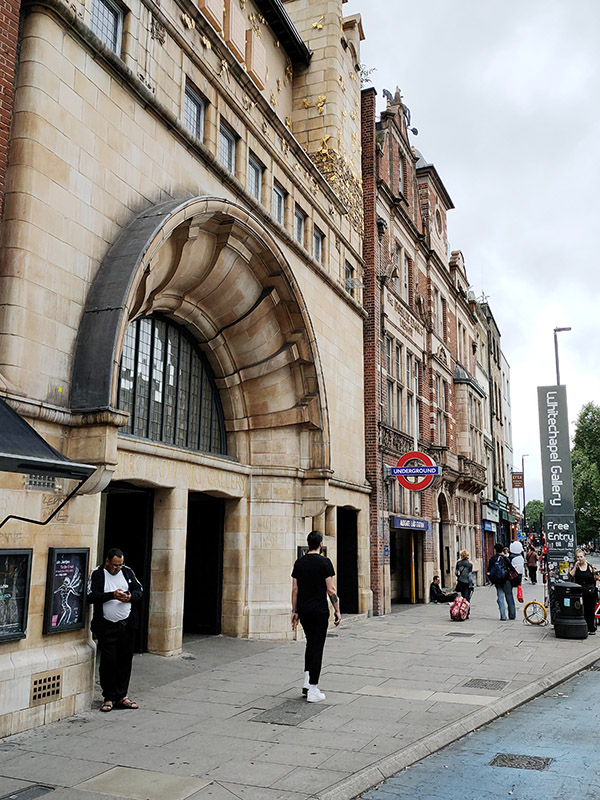
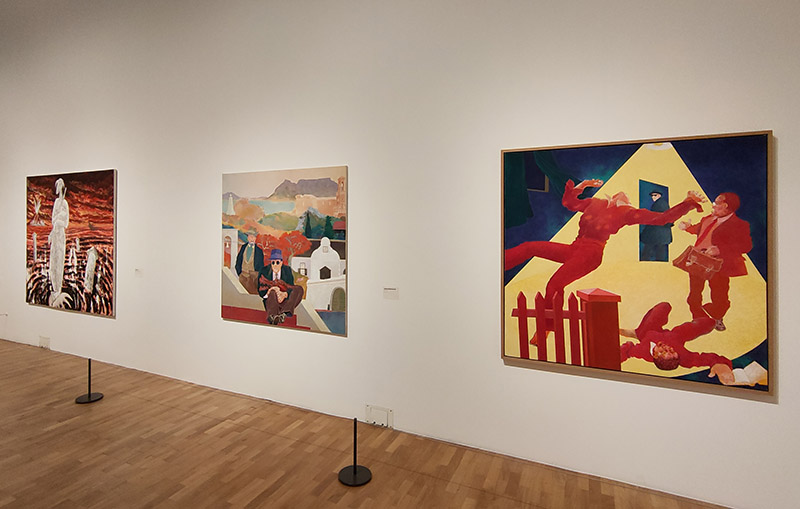
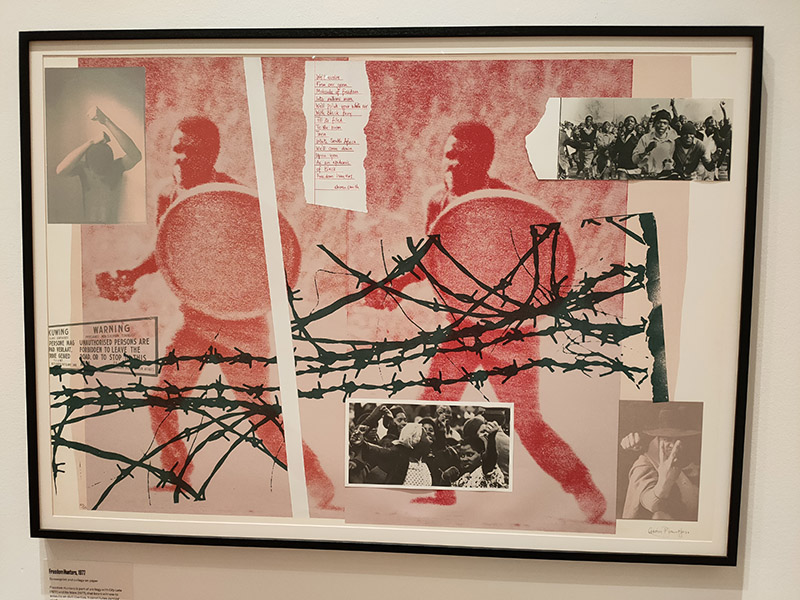
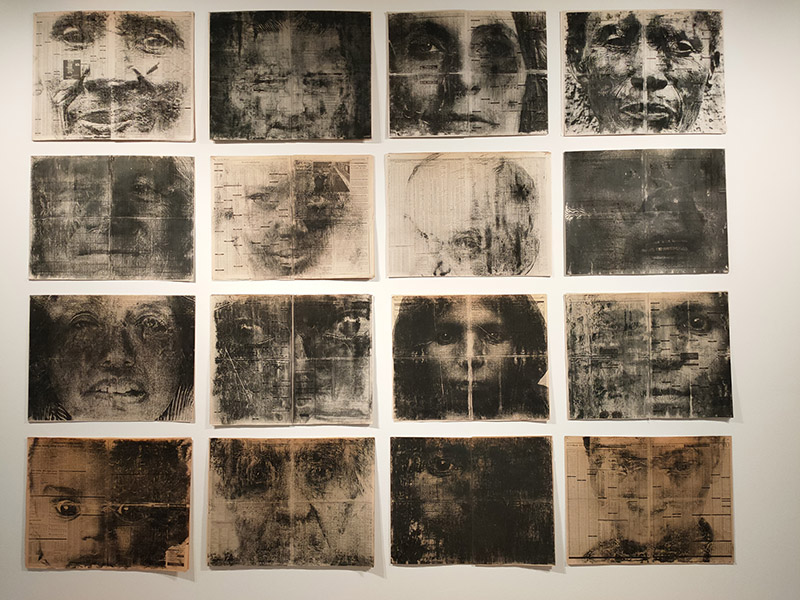
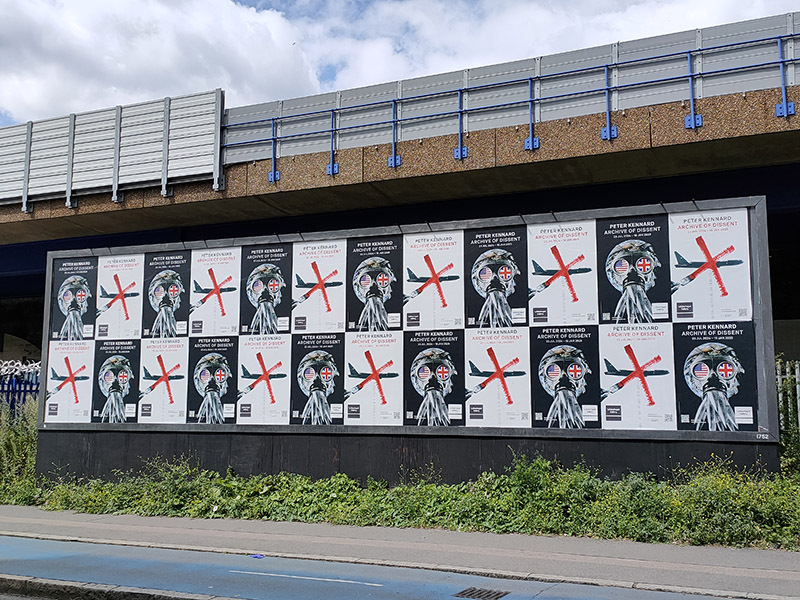
Fortunately, we only have to travel a a short way further for something altogether more edifying. Straddling one of the entrances to Aldgate East tube station, The Whitechapel Gallery was founded in 1901 to present “the finest art of the world for the people of the East End, London”. As a regular visitor over the last three decades I would say it’s made a pretty good fist of keeping to that aim. In 1939, Pablo Picasso’s iconic painting, Guernica, was presented at Whitechapel Gallery, during its only visit to Britain, and the Gallery has consistently premiered ground-breaking shows from artists as diverse as Barbara Hepworth (1954), Jackson Pollock (1958), Gilbert & George (1971), Frida Kahlo (1982) and Sonia Boyce (1988). In 2009 the gallery approximately doubled in size by incorporating the adjacent former Passmore Edwards library building. Its current exhibitions include Gavin Jantjes: To Be Free! A Retrospective 1970 – 2023 (until 1st September 2024) and Peter Kennard: Archive of Dissent (until January 2025). Both are worth seeing and the latter is free to visit.
Beyond the gallery, to the east, is what was once the site of St Mary Matfelon church, popularly known as St Mary’s, Whitechapel. Reputedly, the church was covered in a lime whitewash, which gave rise to the district becoming known by the name, Whitechapel. Last rebuilt in the 19th century, the church was firebombed during the Blitz leading to its demolition in 1952. The site, including the church’s nave’s stone footprint and the graveyard – headstones removed – was subsequently turned into a public park. The park was renamed Altab Ali Park in 1998 in memory of Altab Ali, a 24-year-old British Bangladeshi leather clothing worker, who was murdered on 4 May 1978, in the adjacent Adler Street, by three teenage boys as he walked home from work. Ali’s murder was one of the many racist attacks that occurred in the area at that time. At the entrance to the park is an arch created by David Petersen, developed as a memorial to Altab Ali and other victims of racist attacks.


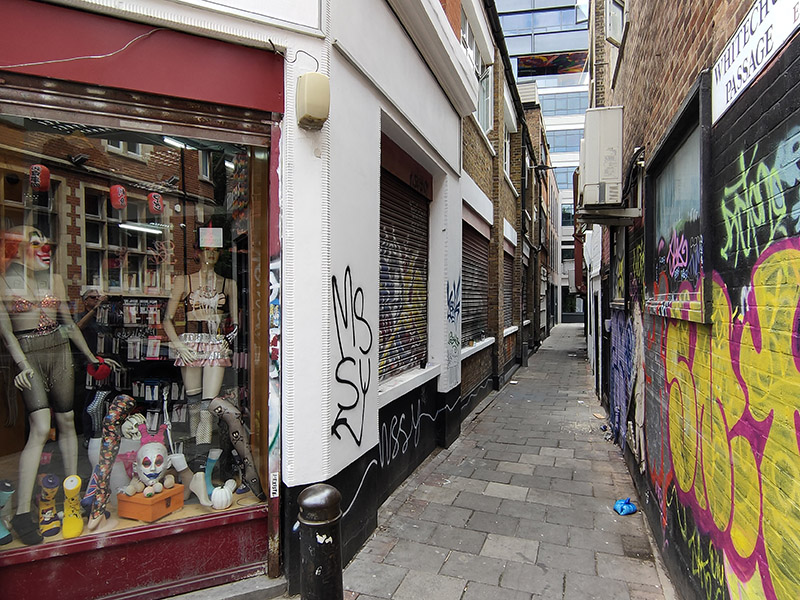
From here we turn southward down White Church Lane, striding swiftly past one of the most disturbing shop windows I’ve seen in a long while (if not ever).
After a brief nod to Assam Street on the left we turn right down Manningtree Street which takes us onto the Commercial Road. At nos.48 -50 Commercial Road is the Proof House which is operated by the Worshipful Company of Gunmakers who have been at this location since 1675 (just 38 years after being granted their charter) though these buildings date from the 19th century. The Proof House has statutory powers to test and regulate the safety of firearms and no gun can be legally sold in the United Kingdom without having undergone proof. It also ensures and certifies that guns wanted for display purposes, rather than use, have been made permanently unusable in the manner required by law and investigates accidents caused by firearms malfunction.
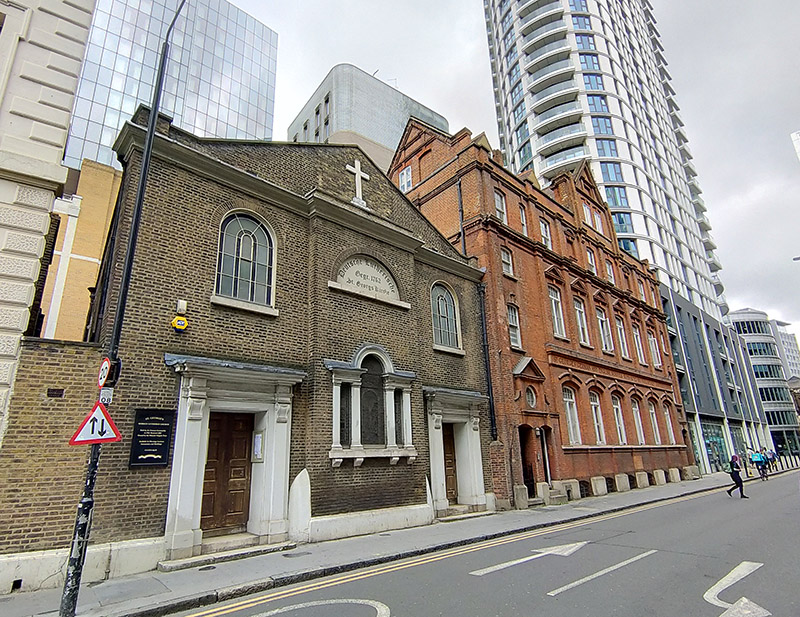
We head away from Commercial Road almost immediately via another stretch of Alie Street. A diversion onto Buckle Street takes us back to Leman Street from where we re-enter Alie Street at the site of St George’s German Lutheran Church. This is the oldest surviving German Lutheran church in the United Kingdom although it ceased to be a place of worship for yer actual German Lutherans in 1995. The founder was Dietrich Beckman, a successful sugar boiler who put up half the money required to buy the site and erect the church. This area of Whitechapel had many sugar refiners of German descent in the nineteenth century and they constituted most of the original congregation.
The area to the south of Alie Street was historically known as Goodman’s Fields and the name has been resurrected for the seven acre food, drink, health and entertainment destination created here on the site of an old postal sorting office within the last few years alongside 1000 new residential properties. There are two gyms, an escape room venue and a Curzon Cinema together with open spaces adorned with sculptural commissions. It looks like it’s been beamed here from another part of London altogether but all those properties have been sold.
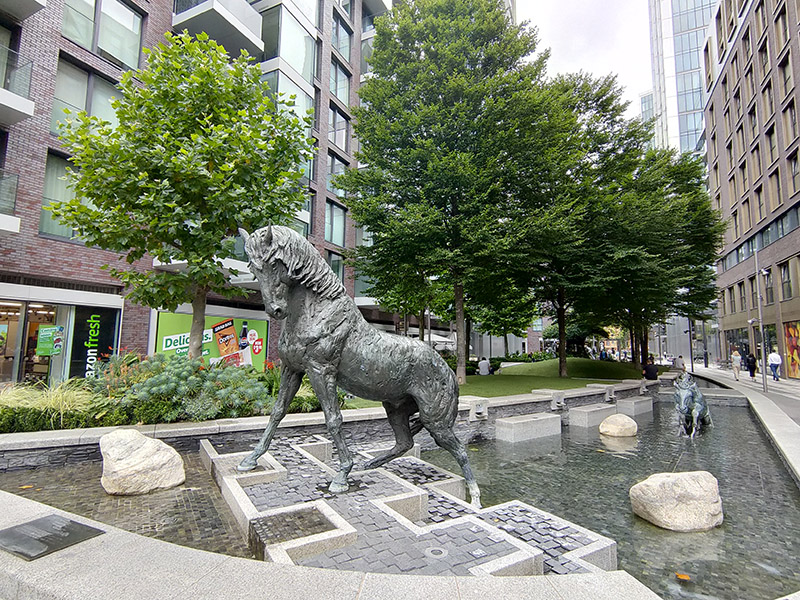
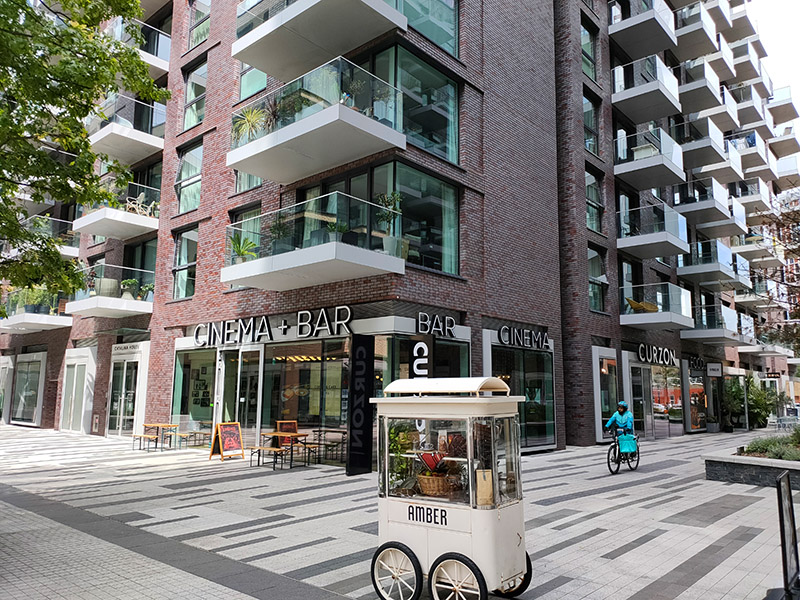


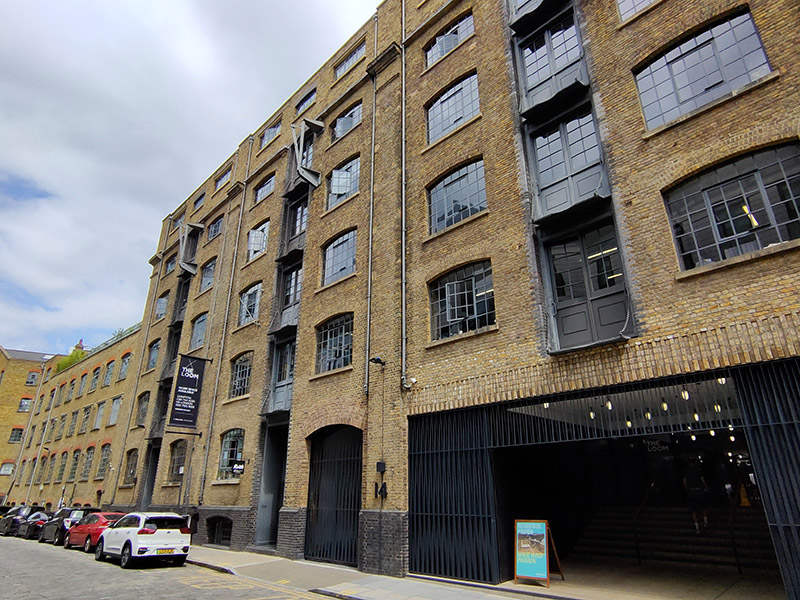
After a stroll through Goodman’s Fields we emerge onto Hooper Street where we turn east and then make our way back to Commercial Road via Gower’s Walk. A former Victorian wool warehouse here has been converted into (or reimagined as) 110,000 sq ft of modern and characterful work space for entrepreneurs, innovators and creative minds known as The Loom.
On returning to Commercial road we turn right then right again onto Back Church Lane. By the junction with Boyd Street stands another repurposed warehouse. This one, originally the property of Charles Kinloch & Co Ltd, wine and spirit merchants, is now apartments.
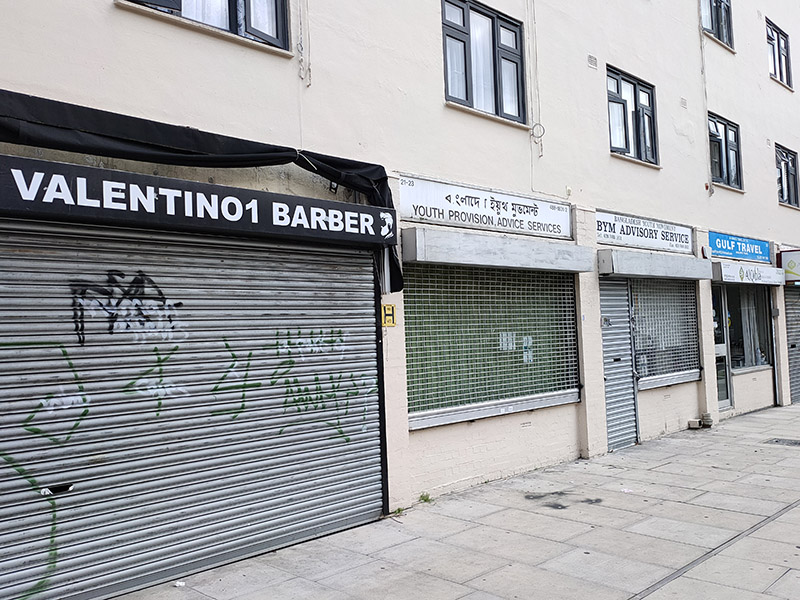
Boyd Street doglegs into Henriques Street where this parade is perhaps another indicator of change in the air.
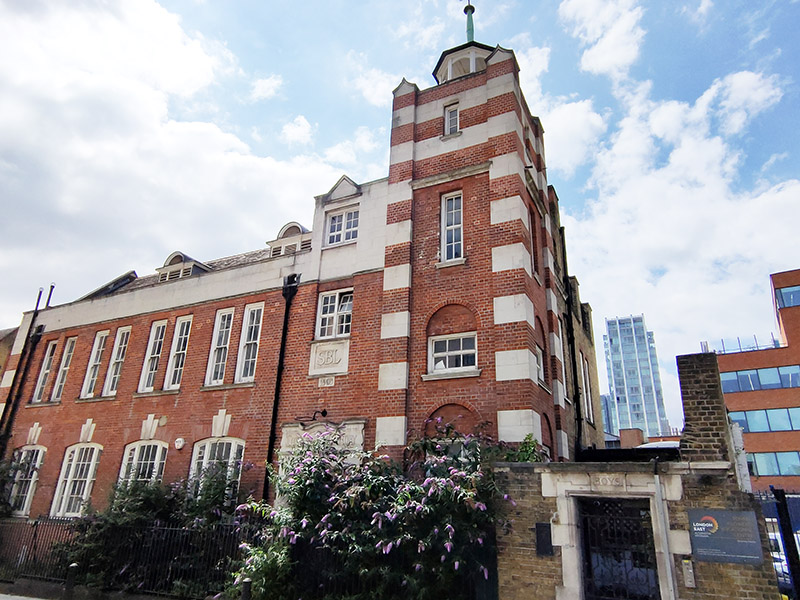
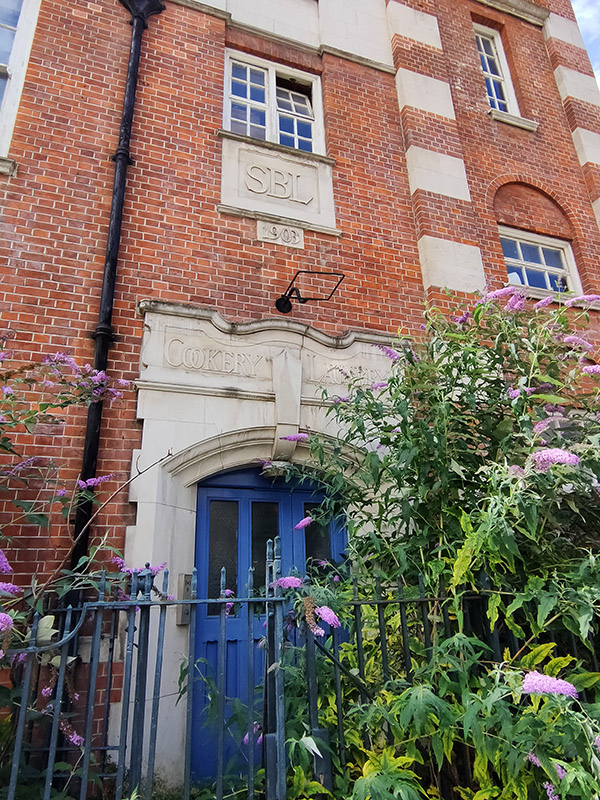
Also on Henriques Street is a building of 1903 vintage that started life as the London School Board Combined Skills centre. In 2010 it was repurposed as An Information and Communications Technology (ICT) centre for young people, and named the Tommy Flowers Centre after the Post Office engineer (1905 – 1998) who in WW2 designed and built Colossus, the world’s first programmable electronic computer, to help decipher encrypted German messages and who was born in Tower Hamlets. After the war Flowers applied for a loan from the Bank of England to build another machine like Colossus but was denied the loan because the bank did not believe that such a machine could work. He couldn’t argue that he had already designed and built many of these machines because his work on Colossus was covered by the Official Secrets Act. Sadly, the Tommy Flowers Centre hasn’t survived in its original guise; for a time it became part of the Tower Hamlets Pupil Referral Unit but at present it appears to be disused.


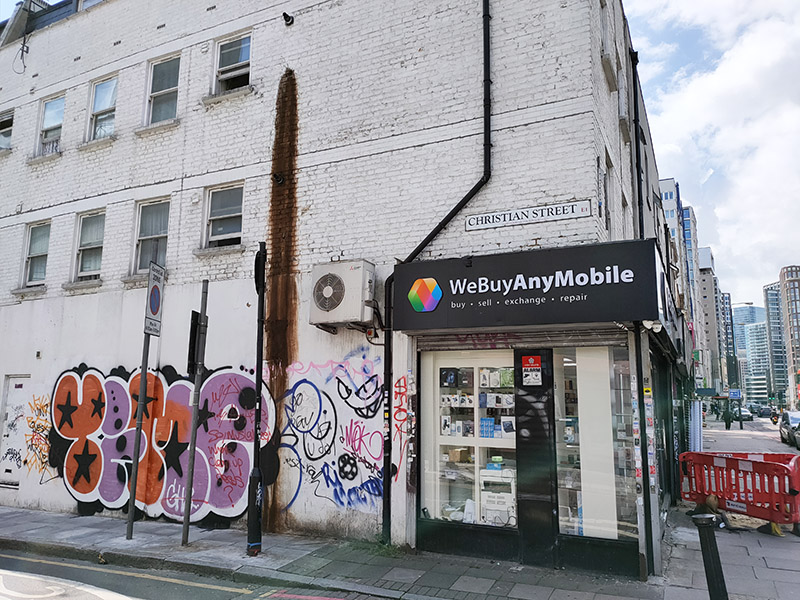
Next street leading south from Commercial Road after Henriques Street is Batty Street which ends at Fairclough Street where we turn east onto Christian Street ( a road out of place and time if ever there was).
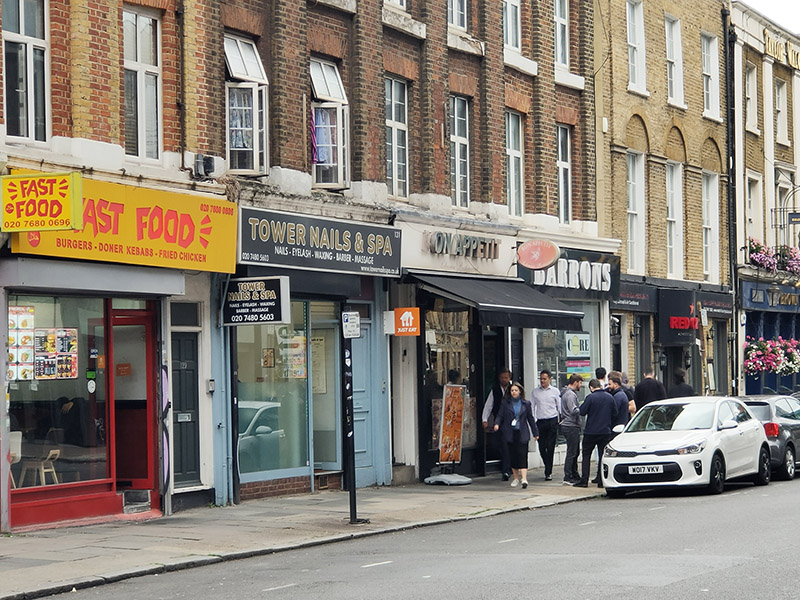
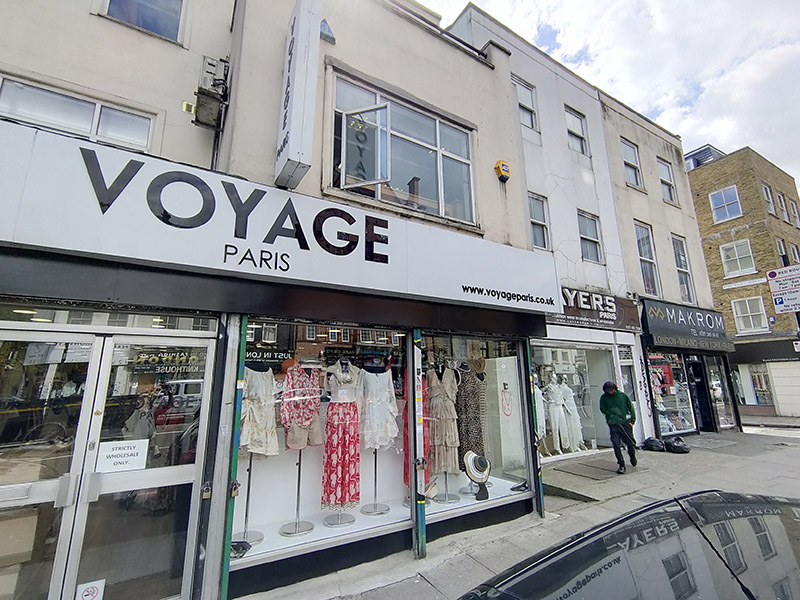
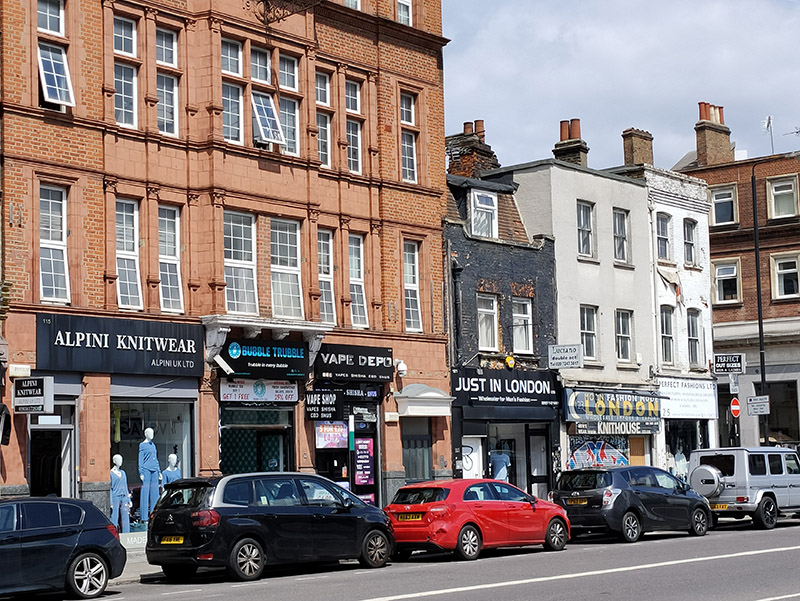
As I’ve probably mentioned before, this part of the East End has had a longstanding association with the garment industry going back to the tailor’s shops of the 19th century Jewish immigrants. Nowadays it’s the Bangladeshi community that has taken on the rag trade mantle and this is in full evidence on Commercial Road in the form of the numerous wholesale fashion outlets that cluster on both sides. Some of these, mainly on the south side, appear to be more than a little disingenuous regarding their international associations. If any of their import or export business actually involves Paris (or New York or Milan) I’d eat one of those frocks. By contrast the operators based on the north side (bottom picture below) are happy to proclaim their parochialism.
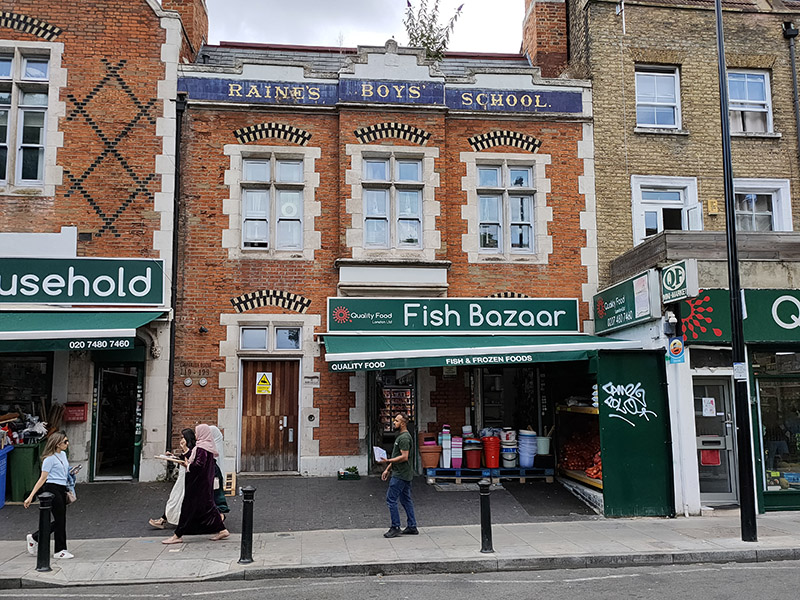
We do one more loop in and out of Commercial Road before we leave it behind. This takes in Umberston Street, Amazon Street and Hessel Street before leading us south on Cannon Street Road. Between 1883 and 1913 this was home to one of the eponymous schools originally established by the philanthropist Henry Raine (who we encountered in the previous post).
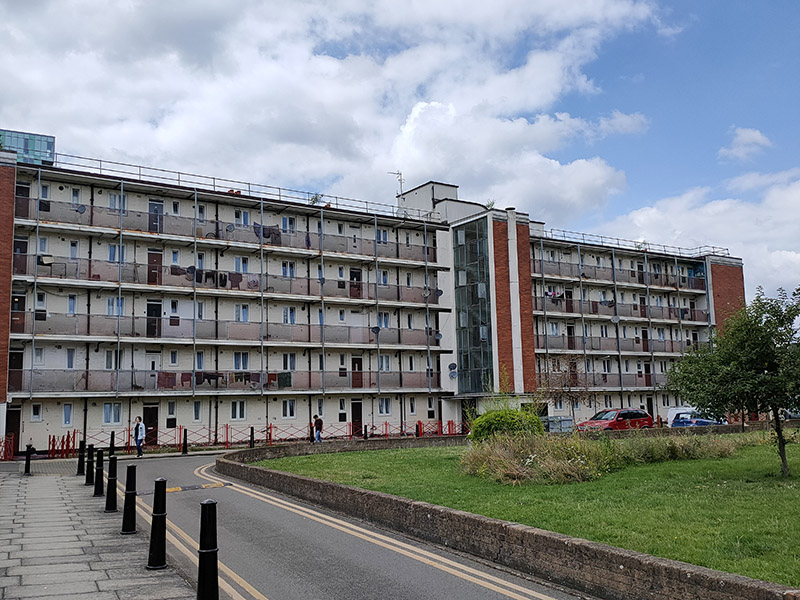
Two thirds of the way to the intersection with Cable Street we turn right onto Ponler Street and then do circuit of Estate Road which unsurprisingly encompasses a social housing estate. I would have expected this to include Walford House (nothing to do with Eastenders) which lies immediately to the west but it transpires this includes some now-private flats which astonishingly (for those of you who live outside of London have a current market value of around £200k.
There follows a sequence of streets with nothing of note to report. To the east of Christian Street we have Langdale Street, Burslem Street, Wicker Street and Golding Street and, to the west, Ellen Street, Strutfield Street and Forbes Street. The latter brings us out onto Pinchin Street which again runs parallel to the DLR line. Here we find a warehouse used by the firm of Pinchin Johnson & Associates Ltd from 1859. Pinchin Johnson was a major supplier of paints and coatings to industry and consumers in the first half of the 20th century and was one of the original constituents of the FT 30 index when this was set up in 1935, although the company had been in existence for 100 years by then. In 1960, PJA was acquired by Courtaulds who, in 1968, merged it with the International Paint business they had acquired earlier in the year.
And that’s us done for the day save for a long stroll along Cable Street and Royal Mint Street back to Tower Hill. (And for the first time in a long while we’ve managed to come in under 3,000 words).