A pretty meaty one this to the say the least; with two of inarguably the three most iconic and important buildings in London to cover off (the third being St Pauls’ Cathedral – sorry, Buckingham Palace). So most of today’s excursion is taken up with visits to the Houses of Parliament (or, more precisely, the Palace of Westminster) and Westminster Abbey, though we did manage to fit in a few actual streets to the south and west of those behemoths before circling back to Parliament Square.
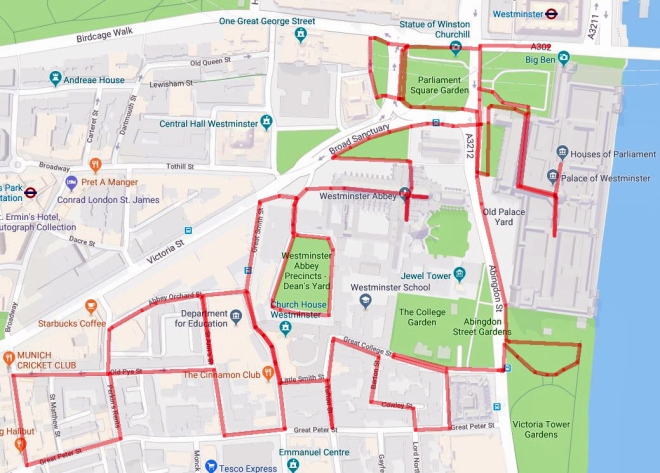
Starting out from Westminster tube station we cross Bridge Street and head along the south side of Parliament Square to the public entrance of the Houses of Parliament at Cromwell Green. After an inspection of my ticket – I’ve booked the audio guide tour – I make my way down the ramp at the bottom of which the airport-style security check awaits. En route we pass the statue of Oliver Cromwell (1599 – 1658), one of only two in the grounds of the Palace of Westminster. The statue was erected in 1899 in the face of fierce opposition from the Irish National Party owing to Cromwell’s ravages against the Catholic population of Ireland. In the end Parliament only approved the statue because an anonymous benefactor, later revealed to be ex-Prime Minister Lord Roseberry, agreed to fund it. After his death Cromwell was originally buried, with great ceremony, in Westminster Abbey. However, following the restoration of Charles II, his body was exhumed and subjected to a posthumous execution and his severed head displayed on a pole outside Westminster Hall (for twenty-four years).

Given the scaffolding in evidence in the picture above, including the complete coverage of Big Ben, this is perhaps the time to note that, after series of protracted debates, both the House of Commons and the House of Lords voted in early 2018 in favour of a temporary decampment from the PoW to allow a long overdue so-called Restoration and Renewal programme to take place. They won’t be vacating the premises until 2025 however so you’ve still got plenty of time to visit before it’s closed down for six years (at least).

First port of call, and where you pick up the audio guide, is Westminster Hall (on the right above minus Cromwell’s severed head). This is the oldest part of the PoW and has, miraculously, survived intact since it was built by William II (aka William Rufus) son of William the Conqueror in 1097. The magnificent oak hammer-beam roof, commissioned in 1393 by Richard II, is the largest medieval timber roof in Northern Europe measuring 68ft by 240ft. In addition to the new roof, Richard also installed statues of every king of England from Edward the Confessor to himself in niches in the walls (only 6 now remain). Ironically, the first event to take place in the hall after Richard’s redevelopments was his own deposition by Henry IV in 1399. On 16 October 1834 a fire broke out in the Palace when two underfloor stoves that were injudiciously being used to destroy the Exchequer’s stockpile of tally sticks ignited panelling in the Lords Chamber. The two Houses were both completely destroyed but Westminster Hall was saved, partly by its thick Medieval walls and partly because the PM, Lord Melbourne, directed the fire fighters to focus their efforts on dousing the Hall’s timber roof.
There are a number of brass plaques embedded in the floor of the Hall commemorating events of historic significance that have taken place there, including the passing of the death sentence on Sir Thomas More in 1535. The stairs at southern end of the Hall were created by architect Charles Barry in 1850 along with a new arch window as part of his post-fire renovations. Turning left at the top of these stairs brings us to the entrance to St Stephen’s Hall above which can be seen the light sculpture New Dawn created by, artist-in-residence, Mary Branson, in commemoration of the campaign for women’s suffrage and unveiled in 2016.
St Stephen’s Hall started life as St Stephen’s Chapel in 1292 and was the in-house place of worship for the reigning Kings of England up to Henry VIII. In 1550, two years after the dissolution of the monasteries, Henry’s son Edward IV gave the chapel over to the House of Commons for use as their debating chamber. The chapel was destroyed by the fire of 1834 and was reconstituted as St Stephen’s Hall as part of Charles Barry’s restoration work. Following the destruction wrought during WWII the hall once again became the venue for sessions of the Commons from 1945 to 1950 while the Commons Chamber was being rebuilt.
On either side of the Hall are statues of famous parliamentarians including John Hampden, Robert Walpole, William Pitt and Charles James Fox and on either side of the doorways are statues of early Kings and Queens of England. The paintings on the walls depict various important events in British history, while the ten stained-glass windows, five on either side, depict the arms of various parliamentary cities and boroughs; these were damaged in air raids during the Second Word War and since restored.
St Stephen’s Hall represents the last opportunity to take photographs inside the Palace of Westminster; beyond here it’s strictly verboten. As a consequence I won’t dwell too long on the rest of the tour which takes us into the Central Lobby where we turn right to pass through the Peers Lobby, the Lords Chamber, the Royal Gallery and the Robing Room and back again. Traversing the Central Lobby for a second time gains access to the Members Lobby and the Commons Chamber. Now on the day of my visit neither of the Houses was sitting so it was possible to get right in among the green and red benches (though of course you’re not allowed to sit on them). When either of the Chambers are in session visitors can, of course, view the debates from the respective public galleries – no tickets required except for PMQs. The visitor’s gallery in the Commons is formally known as the Strangers’ Gallery. Back in the 1930’s according to my guidebook “any Foreigners desirous of listening to a debate” needed to apply to their Ambassadors”. There was also a separate Ladies’ Gallery back then though persons of the female persuasion had recently also been granted access to the main viewing gallery. The grilles referred to below were installed over the windows in the Ladies’ Gallery (earning it the nickname “the Cage”) so the women could see out but men could not see in, and therefore not be distracted by the women watching them. They were removed in 1917 following a petition from the London Society for Women’s Suffrage and just a couple of months after the passing of the bill giving the vote to women over the age of 30.

Once the tour is over we leave the HoP and head across to the South-West corner of Parliament Square and follow Broad Sanctuary down to the entrance to Westminster Abbey. As ever my timing is the complete opposite of impeccable since if I’d just waited a couple more weeks then the Queen’s Diamond Jubilee Galleries would have been open. Reached via the newly-built Weston Tower, the first major addition to the abbey since 1745, these apparently offer stunning views down into the nave of the church as well as housing 300 treasures from the Abbey’s collection selected to reflect it’s thousand-year history. Still, I expect the queues are going to be absolutely horrendous. It’s busy enough on the day of my visit though having pre-booked a ticket online I get in pretty quickly. At £20 a time (£22 if you buy on the day) the revenue from visitors to the Abbey is probably sufficient to keep the Church of England solvent all on its own. Despite the crowds it’s not that unpleasant shuffling round; I suspect it’s the free audio guides rather than piety that keeps the noise to a minimum and the no-photography rule is universally adhered to.
Westminster Abbey can trace its origins back to the middle of the eleventh century when Edward the Confessor built a new stone church dedicated to St Peter alongside an existing Benedictine monastery founded around a hundred years earlier. This church became known as the “west minster” to distinguish it from St Paul’s Cathedral (the east minster) in the City of London. Unfortunately, when the new church was consecrated on 28 December 1065 the King was too ill to attend and died a few days later, his mortal remains being entombed in front of the High Altar. This set something of a trend since when King Henry III (1207 – 1272) had the Abbey rebuilt in the new Gothic style he died before the nave could be completed. Henry did however have time to transfer the body of Edward the Confessor (by then sanctified as Saint Edward) into a more magnificent tomb behind the High Altar in the new church. This shrine survives and around it are buried a cluster of medieval kings and their consorts including Henry III himself, Edward I and Eleanor of Castile, Edward III and Philippa of Hainault, Richard II and Anne of Bohemia and Henry V. Westminster Abbey is of course irrevocably linked with the history of the English/British monarchy. Every monarch since William the Conqueror has been crowned in the Abbey, with the exception of Edward V and Edward VIII (abdicated) who were never crowned. The ancient Coronation Chair can still be seen in the church. Elizabeth I was buried in the vault of her grandfather, Henry VII, in the so-called Lady Chapel which he had constructed in 1516. Her successor, James I, didn’t attend her funeral service but he later had a white marble monument erected in her memory in a chapel adjacent to the Lady Chapel. Although a few years after that he had a taller and grander memorial installed for his mother, Mary Queen of Scots.
But it’s not just royalty that’s buried and/or commemorated in the Abbey of course. When Geoffrey Chaucer was buried here in 1400 it was because he was Clerk of The King’s Works not for his literary achievements. However, nearly 200 years later, when Edmund Spenser (of Faerie Queene fame) asked to be buried next to Chaucer the concept of Poet’s Corner was born and continues to this day. Deciding which dead writers merit the honour of being immortalised in Poet’s Corner is the prerogative of the Deans of Westminster. Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, Handel and Laurence Olivier are among those whose actual remains lie here while Shakespeare, Jane Austen, the Bronte sisters, Lord Byron and a host of others are memorialised in brass or stone. The most recent additions to the pantheon include Ted Hughes, Philip Larkin and David Frost.
As I noted already there’s no photography allowed inside the abbey so the next selection of photographs are all of or from within the College Garden and the Little Cloister Garden. Before we get to that those though I just wanted to record one personal highlight of the tour which is the murals in the Chapter House. These were painted in the late 14th century at the instigation of one of the monks of Westminster, John of Northampton, and depict scenes from the New Testament’s Revelation of St John the Divine (otherwise known as the Apocalypse). Only fragments of the paintings remain and many of those that do are extremely faint but this ghost-like appearance only adds to their macabre impact.
We exit the Abbey on its west side opposite the Crimea and Indian Mutiny memorial which sits inside a triangular island created by Victoria Street and The Sanctuary. Turning south we pass through the gatehouse of the octagonal turreted building known as The Sanctuary built to the design of Sir George Gilbert Scott in 1853-54. Nowadays this accommodates the Deanery of the Abbey and also the Attorney Generals’ Office.


On the other side of the gatehouse is Dean’s Yard which comprises most of the remaining precincts of the former monastery of Westminster, not occupied by the Abbey buildings. The East side consists of buildings occupied by Westminster School, the South by Church House, the headquarters of the Church of England and the West by Westminster Abbey Choir School.
Historically the Abbey was one of the last ecclesiastical sanctuaries to surrender its ancient rights, with the result that the precincts were largely occupied by the most undesirable and dangerous of inhabitants. They were held in check by the Abbot’s own penal jurisdiction, and by the knowledge that the Abbot could instantly expel them to their fate at the hands of the Common Law. Westminster School displays a royal pardon of Charles II for the King’s Scholars who murdered a bailiff harassing the mistress of one of the scholars in Dean’s Yard, allegedly in outrage at the breach of traditional sanctuary although it had been legally abolished by then.
After a circuit of Dean’s Yard we leave the same way we came in, head back up to Victoria Street and after a few steps to the left turn south down Great Smith Street. Take a right next into Abbey Orchard Street past the Department of Education building and down to the end where it forks in two by Companies House. This unprepossessing building is just the London office and information centre; the actual Registrar of Companies (for England & Wales) is down in Cardiff.

Taking the left fork we drop down onto Old Pye Street and continue west. On reaching Strutton Ground we turn south as far as Great Peter Street where we head back eastward. On the corner with Perkin’s Rents we have today’s pub of the day (the first in a long while), The Speaker. Aptly-named given its location of course and though it doesn’t look much from the outside the interior is salubrious enough and they do a damn fine bacon, brie and onion chutney bagel to go with a decent selection of beers. Used by male House of Commons researchers as a venue for mansplaining to their female colleagues (on the evidence of this one visit).

In Victorian times, the area round here was a notorious slum known as the Devil’s Acre. The houses were mostly occupied by what a contemporary described as “mendicants, hawkers, costermongers, lodging house keepers, thieves and abandoned females of irregular and intemperate habits” and it wasn’t unusual for 10 to 12 people to share a room. The slum was cleared from 1877 onward and the Peabody Trust built one of their estates to replace a large part of it.
We pass through the middle of the estate up Perkin’s Rents back to Old Pye Street then follow that east to its junction with St Ann’s Street and turn south back down to Great Peter Street. Here we turn east as far as Great Smith Street and head north towards the Abbey again. On the west side of the street is the Westminster Library which when it was built in 1891 incorporated a public baths and wash house. The baths themselves were removed in 1990 when that part of the building was turned into the Westminster Archive Centre but if you look in the top left corner of the picture below you can see the original sculpted panels of swimmers created by Henry Poole (1873 – 1928).

We turn right opposite into Little Smith Street which runs through to Tufton Street. At no.11 resides J. Wippell & Company, suppliers of clerical vestments and church furnishings. The Wippell family set up in business in the West Country in 1789 but this London shop was established just over a hundred years later.

Proceeding north up Tufton Street brings us to Great College Street where we turn right briefly, past the southern end of Westminster School, before diverting into Barton Street. Barton Street and Cowley Street, which comes off it at a right angle, are fertile ground for blue plaque hunters. No.14 Barton Street is the one-time home of T.E Lawrence (1888 – 1935) better known of course as Lawrence of Arabia. Lawrence lived here while writing Seven Pillars of Wisdom and account of his experiences working for British Military Intelligence in the near east during WW1.
Round the corner at no.6 Cowley Street Lord Reith (1889 – 1971), the first Director-General of the BBC, lived from 1924 – 1930. Despite having no broadcasting experience (though it’s hard to see where he would have got any at that time) he got the job as general manager of the newly formed BBC in 1922 and stayed in the lead role until 1938. He is memorialised by the BBC’s annual series of Reith Lectures which began in 1948.
Across the road no.16 was the home of legendary luvvie Sir John Gielgud (1904 -2000) from 1945 to 1976. Gielgud’s career spanned almost 80 years, ranging from leading roles in Hamlet and King Lear on the stage to playing the butler to Dudley Moore’s Arthur for which he won an Oscar for Best Supporting Actor.
Nothing to do with these famous ghosts but if I could have my pick of somewhere to live in London then Barton Street / Cowley Street would be very high up on the list.
There’s a small second section of Cowley Street, perpendicular to the main stretch, which emerges back out on Great Peter Street. Then the next northward turning is Little College Street which takes us back to Great College Street from where it’s a short hop east to Abingdon Street, on the other side of which are the Victoria Tower Gardens. At the entrance to the gardens stands the memorial to the mother and daughter leading lights of the Suffragette movement, Emmeline (1858 – 1928) and Christabel (1880 – 1958) Pankhurst. The main feature of the memorial is a bronze statue of Emmeline by Arthur George Walker which was unveiled in 1930. Shortly after Christabel’s death the statue was moved to its present location and bronze reliefs commemorating her achievements were added.

On the river embankment wall is a green plaque in memory of Sir Thomas Pierson Frank (1881 – 1951) who as Chief Engineer for the London County Council during WW2 directed repair operations to public infrastructure including the Thames wall such that although this was hit at least 121 times during the war years the city never flooded.
Above left is a shot of the southern end of the Palace of Westminster showing the Victoria Tower after which the gardens are named. I mentioned earlier that there were just two statues in the grounds of the PoW and we pass the second of those as we return towards the Palace via Abingdon Street and through Old Palace Yard. The equestrian statue of Richard I (popularly known as Lionheart or Coeur de Lion) was created by Baron Carlo Marochetti (who collaborated with Landseer on the Trafalgar Square lions if you remember). The statue was originally produced in clay for the Great Exhibition of 1851 then funds were raised to enable it to be cast in bronze and it was installed in Old Palace Yard in 1860.
Having arrived back at the HoP we cross the road again and set off on an clockwise circuit of Parliament Square. Plans for the Parliament Square Garden were included in Charles Barry’s design for the new Houses of Parliament following the 1834 fire but the gardens weren’t laid out until 1868. The first batch of statues were erected between 1874 and 1883 as monuments to the nineteenth century Prime Ministers; the Earl of Derby, Viscount Palmerston, Robert Peel and Benjamin Disraeli. Most of the others were installed after the post-WWII redesign of the garden to commemorate both giants of 20th century British parliamentary history and iconic world statesmen. So, in the slides below, we have, respectively :
- Nelson Mandela, sculpted by Ian Walters (2007) in the foreground with Sir Robert Peel sculpted by Matthew Noble (1876) beyond him and in the background Abraham Lincoln (1920).
- Mahatma Ghandi sculpted by Philip Jackson (2015) in the foreground and Benjamin Disraeli sculpted by Mario Raggi (1883) behind him.
- The most recent addition to the pantheon and the first woman to be granted the honour – Dame Millicent Fawcett (1847 – 1929) sculpted by Gillian Wearing (2018). The statue was erected to coincide with the centenary of women being granted the vote. Millicent Fawcett was a leader of the suffragist arm of the campaign for votes for women who were less militant than the suffragettes though unlike the suffragettes they didn’t call a halt to their campaigning during the First World War. The words on the banner her statue holds are from a speech she made after the death of suffragette Emily Wilding Davison.
- George Canning sculpted by Sir Richard Westmacott (1832 but moved to its present location in 1949).
- David Lloyd George sculpted by Glynn Williams (2007)
- Winston Churchill sculpted by Ivor Robert-Jones (1973)
Final port of call for today is the Supreme Court Building which stands on Little George Street which runs parallel with the west side of the square. The building, originally known as the Middlesex Guildhall, dates from 1913 and was designed in the neo-gothic style by Scottish architect, James Gibson. The Supreme Court is the highest court of appeal in the UK but it has only been in existence since 2009; prior to that the House of Lords (or rather the Law Lords) occupied the top-tier of the British legal pyramid. It was the Constitutional Reform Act of 2005 that led to the creation of the Supreme Court in order to fully separate the legislature from Parliament. The Supreme Court doesn’t conduct trials as such; it sits in order to determine whether the correct interpretation of the law has been applied in civil cases that are referred to it for appeal. The Justices of the SC, currently numbering eleven and appointed by an independent selection commission, determine which cases they will hear based on the extent to which they raise ‘points of law of general public importance’. The same 11 justices also form The Judicial Committee of The Privy Council (JCPC) which is the court of final appeal for the UK’s overseas territories and Crown dependencies, as well as many Commonwealth countries.

















