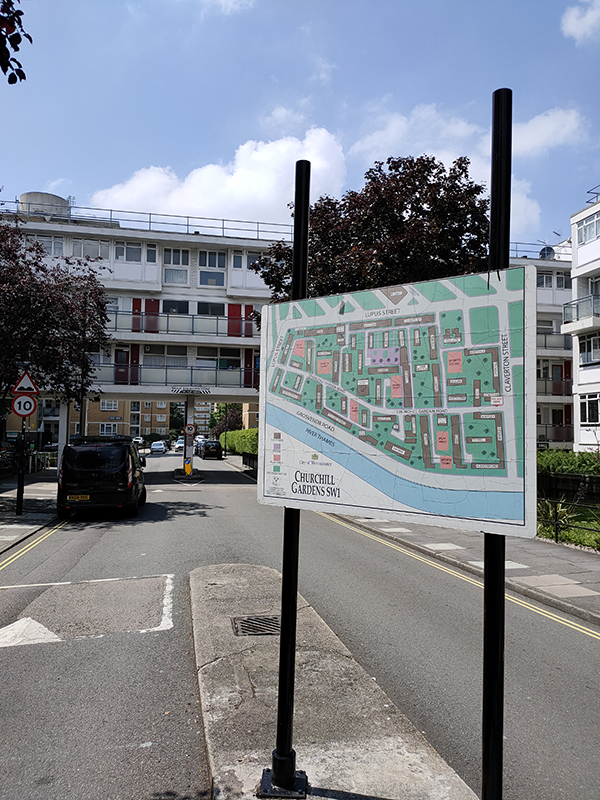
As some of you may recall from the Ealing comedy “Passport to Pimlico” this part of London likes to consider itself as something of a self-contained unit. There is some justification for this in that, not only are, its boundaries clearly delineated by Vauxhall Bridge Road, the mainline out of Victoria Station and the River Thames but it was first fully developed as part of the Grosvenor Estate after 1825. To partly reiterate what we covered last time out, Robert Grosvenor, First Marquess of Westminster, appointed Thomas Cubitt, master builder, to create a new district on land reclaimed using the soil excavated during the construction of St Katharine’s dock. Like Belgravia this was based on a grid of attractive terraces built in the Regency style but unlike its more fashionable neighbour to the north Pimlico largely drew its residents from the middle classes. From the end of the 19th century onwards the demographic profile of the two areas moved farther apart and parts of Pimlico came close to being designated as slums though this was mitigated by a number of new public housing projects. The 20th century then saw the creation of two large but contrasting developments facing the river, Dolphin Square and the Churchill Gardens Estate. The white stucco terraces are still around today of course, street after street of them (sigh). Some of them are still single occupancy townhouses, many others have been converted into flats and a number are now used as budget hotels. What is striking about the area (even though this is far from unique in London) is the cheek-by-jowl existence of multi-million pound private properties and social housing units.
Apologies for the lengthy preamble but it will, hopefully, save time later on.
Fittingly, Pimlico tube station is our starting point for today. We kick off by heading, via Drummond Gate, down to Bessborough Gardens a garden square developed in the 1980s in a pastiche of the Cubitt-style. The Queen Mother’s fountain in the gardens has a supposed dolphin motif though it’s actually a pair of entwined sturgeon (no relation).
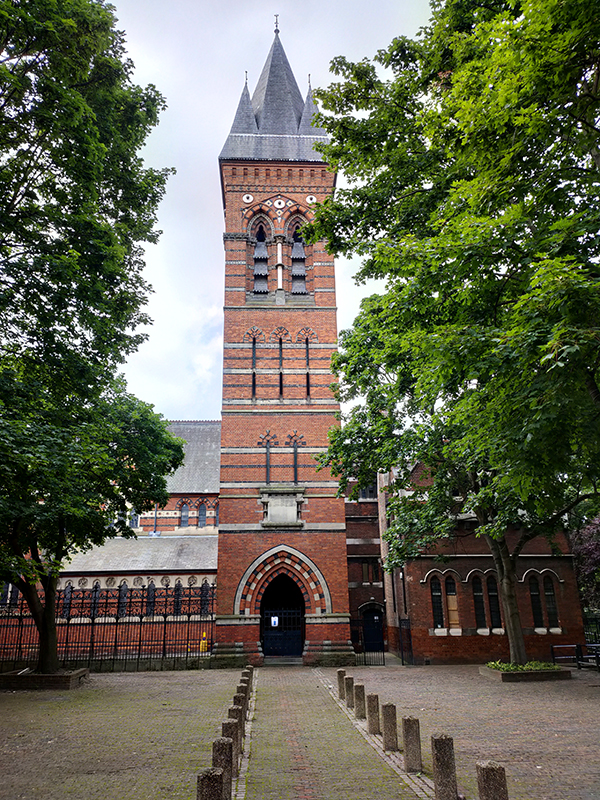
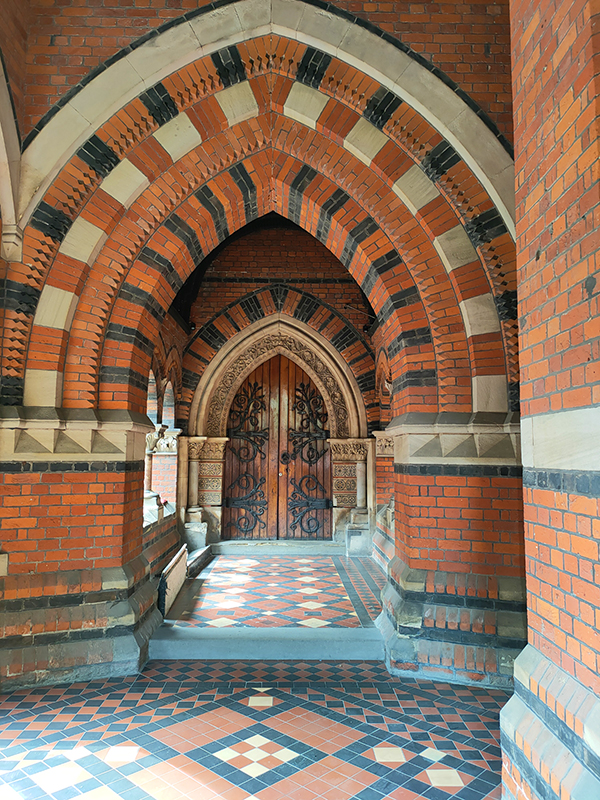
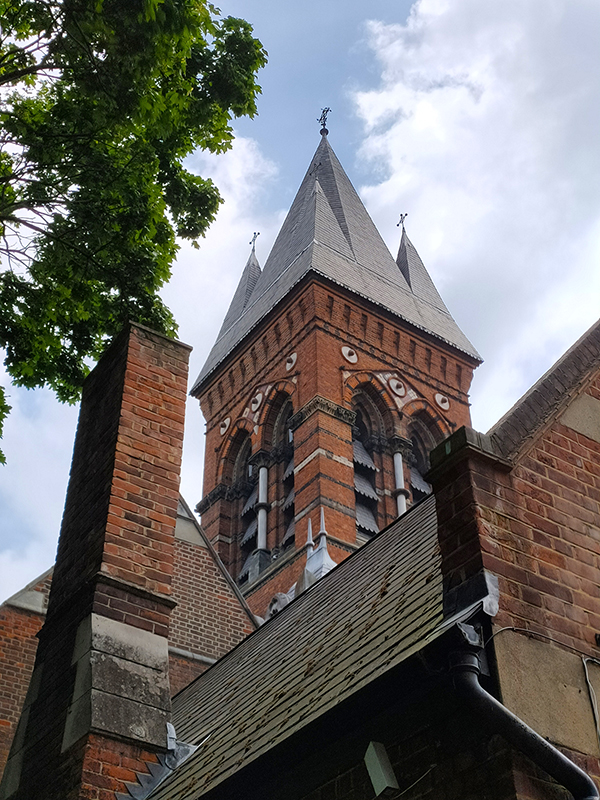
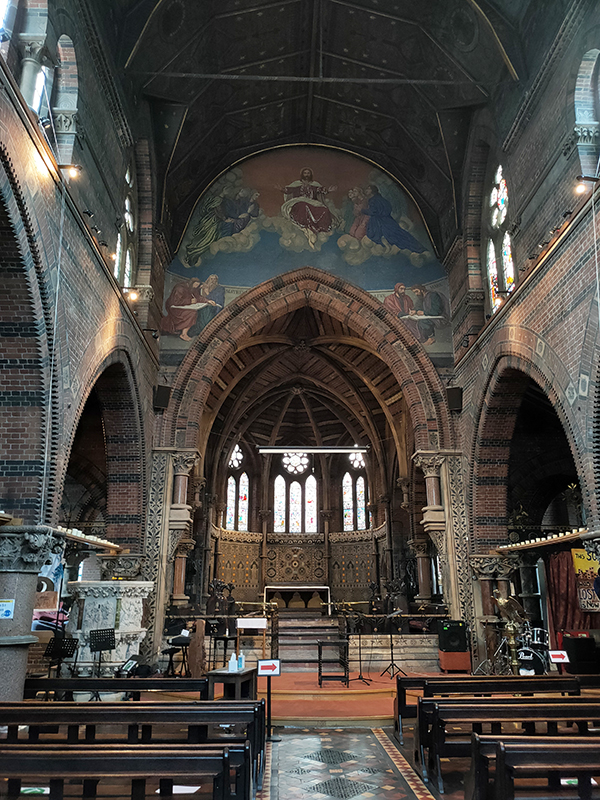
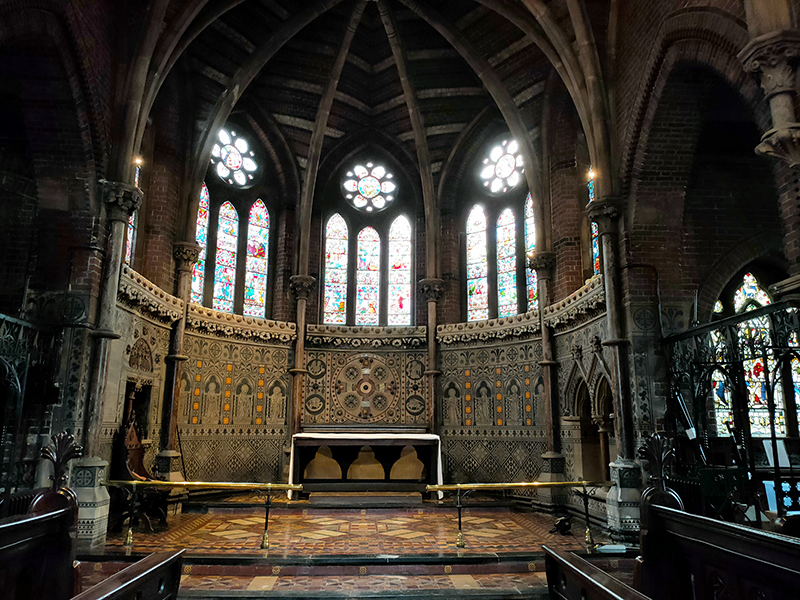
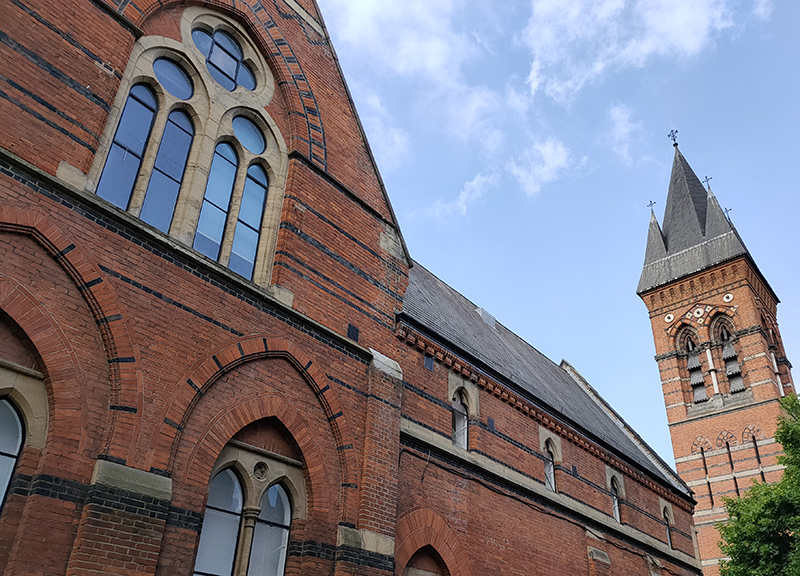
To the west of Bessborough Gardens, reinforcing the point I made earlier, an upscale mid-1990’s development and the Peabody Trust’s Tachbrook estate sit side by side. Navigating around and between these involves Bessborough Place, Balvaird Place, Lindsay Square and Balniel Gate. After this circuit we return to the tube station and take Rampayne Street into Vauxhall Bridge Road. North for a bit then turn left into Moreton Street where we discover the Gothic revival marvel that is the Church of St James the Less. This now grade I listed C of E church was built in 1858–61 by George Edmund Street who was commissioned by the three daughters of the recently deceased Bishop of Gloucester, James Henry Monk. Constructed predominately in brick, its most prominent external feature is its free-standing Italian-style tower, while its interior incorporates design themes which Street observed in medieval Gothic buildings in continental Europe. When I arrived the building was closed but I rang the buzzer on the off-chance and a very simpatico lady allowed me to pop in for a look at the moody interior.
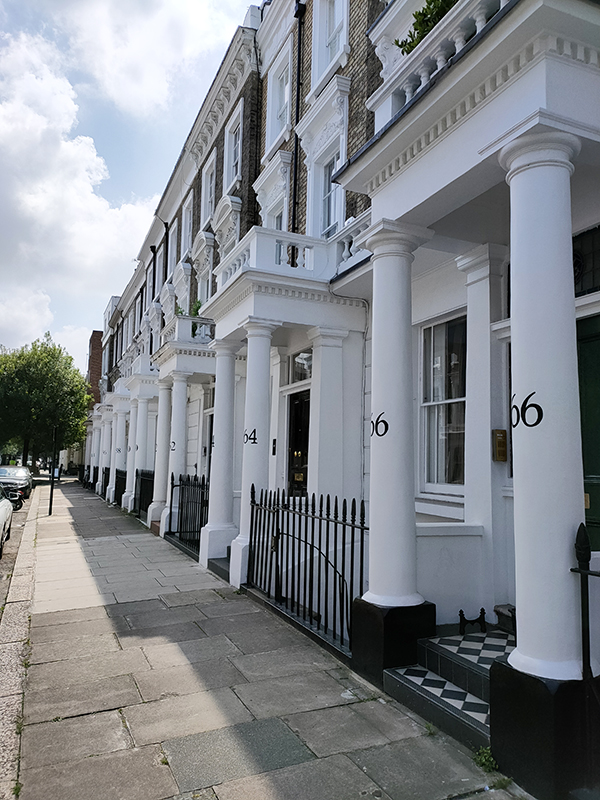
After visiting the church we turn north again up Tachbrook Street alongside the Lillington Gardens Estate to the east. On the other side are those familiar townhouses so the next shot is an attempt to illustrate the dichotomous nature of the area’s housing that I’ll keep harping on about (probably).
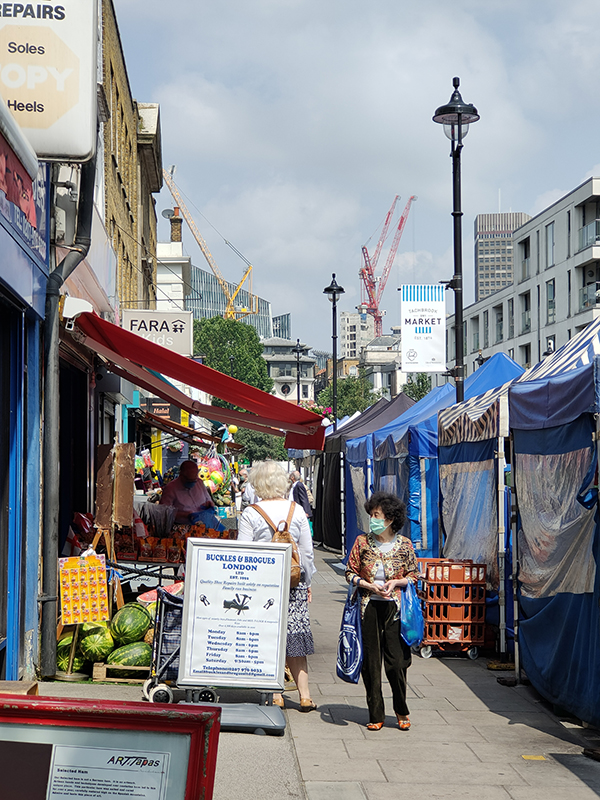
Beyond the estate we take Charlwood Street back onto VBR then resume northward as far as Warwick Way before rejoining Tachbrook Street for the section that contains the eponymous market.
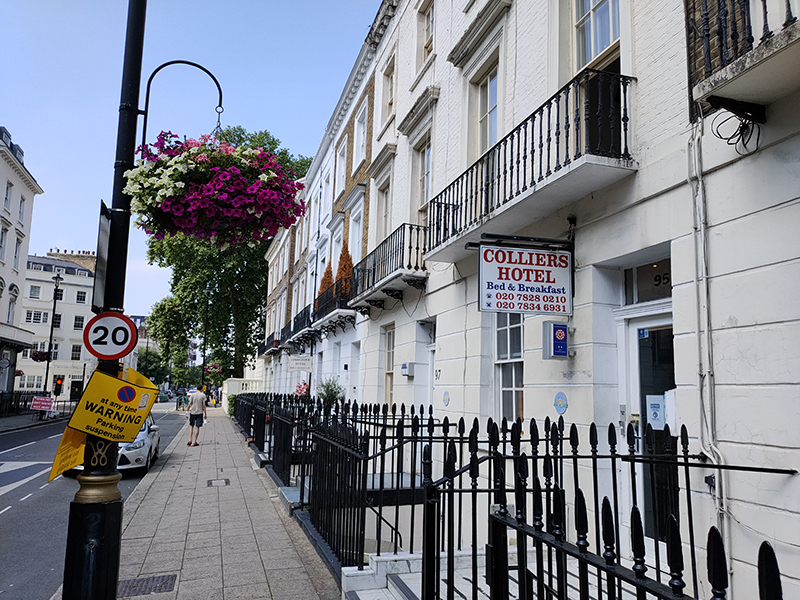
A sequence of Charlwood Place, Churton Street, Churton Place and Denbigh Street help us back on to Warwick Way from where we make our way west to St George’s Drive and then Eccleston Square. Warwick Way is particularly blessed with those budget hotels I mentioned earlier.
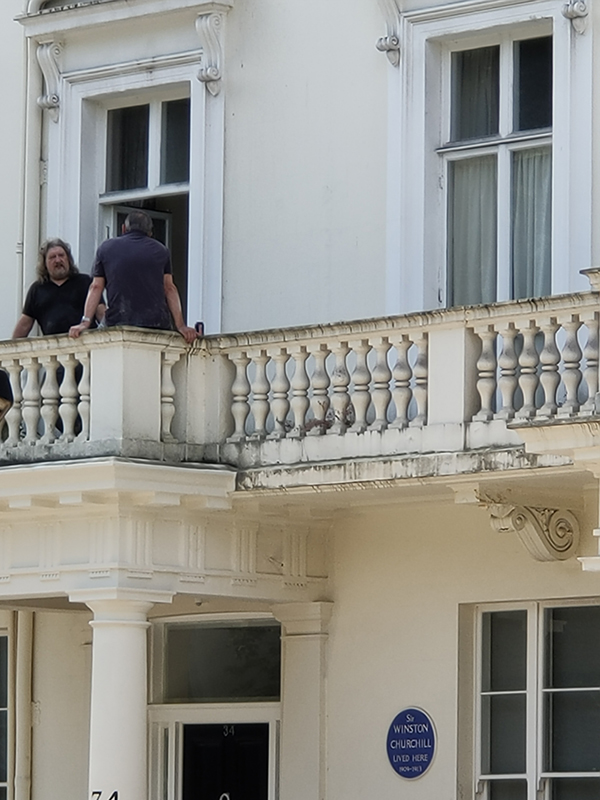
Eccleston Square, like its counterparts in Belgravia was built by Thomas Cubitt in the 1830’s. Its communal private gardens have been grade II listed since 1987 and since Wimbledon was on the tennis courts were actually being used. Winston Churchill lived at no.33 (the St George’s Drive end) from 1909 – 1913. He moved there with Clementine a year after they married and their first two children were born there.
North of Eccleston Square, Hugh Street runs parallel and crosses over St George’s Drive to get to Cambridge Street and Alderney Street which offer more of the same. (See below but you’ve probably got the idea by now)
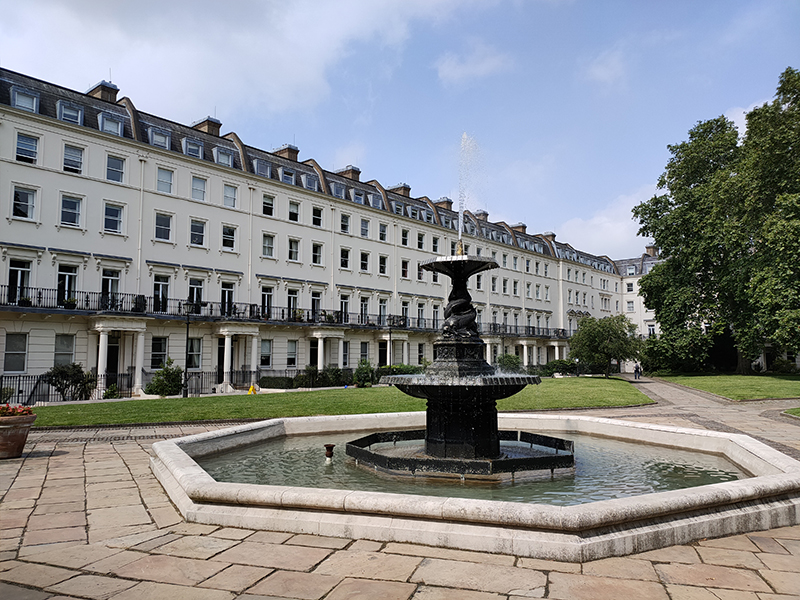
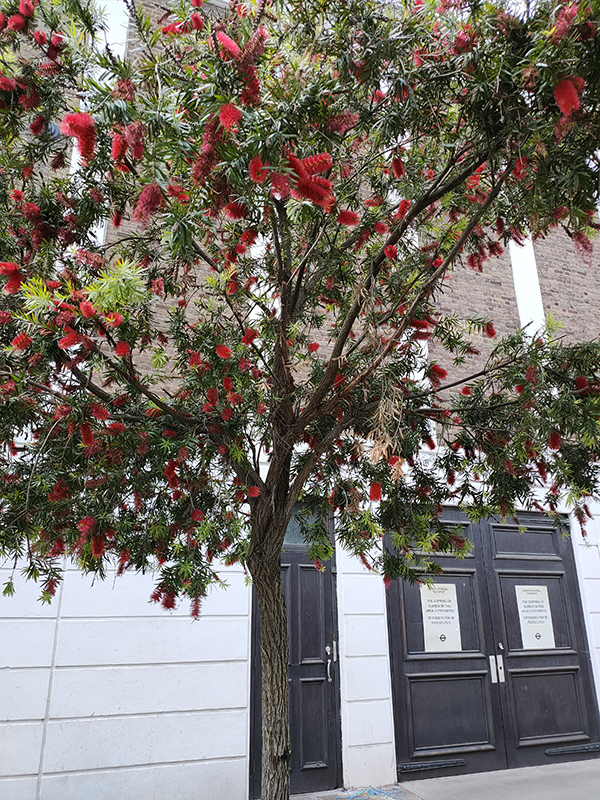
Heading west again, the last stretch of Warwick Way ends at the junction of Ebury Bridge and Sutherland Street. We turn left onto the latter then left again into Sutherland Row and work our way back to St George’s Drive via Cumberland Street, Cumberland Court, Winchester Street and Clarendon Street. Warwick Square is the final garden square in the parallel running sequence that began with Eaton Square. Like the others its gardens are private and Grade II listed along with the buildings. Many of the latter are now commercial rather than residential premises. Cubitt himself lived at no.66 while the square was being developed in the 1860’s. After a circuit of the square we travel via Gloucester Street and Moreton Place to the southern section of Moreton Street with its high class boutiques and eateries. Moreton Place and the adjacent Moreton Terrace are lined with these splendid red-flowering trees which I believe (having looked it up) are Crimson Australian Bottle Brush aka Callistemon citrinus splendens. I wonder if Arabella Lennox-Boyd had a hand in that.
After Moreton Terrace we duck in and out of St George’s Drive using stretches of Denbigh Street, Charlwood Street and Denbigh Place. At no.63 St George’s Drive is a blue plaque commemorating the one year (1896) residency of Hindu philosopher Swami Vivekananda ( 1863 – 1902). Vivekananda was a chief disciple of the 19th-century Indian mystic Ramakrishna and was instrumental in the introduction of the Indian philosophies of Vedanta and Yoga to the Western world. He was a major force in the contemporary Hindu reform movements in India, and contributed to the development of nationalism in colonial India. In 1893 he represented India and Hinduism at the World’s Parliament of Religions in Chicago.
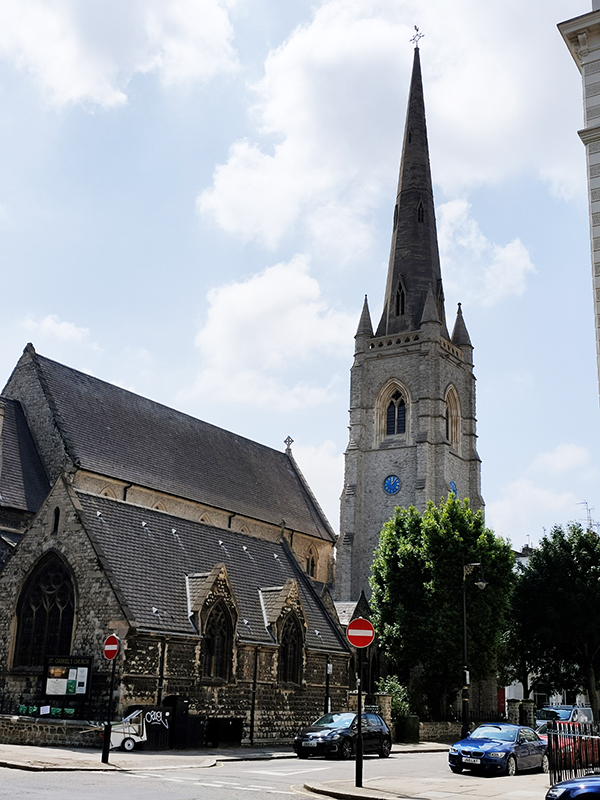
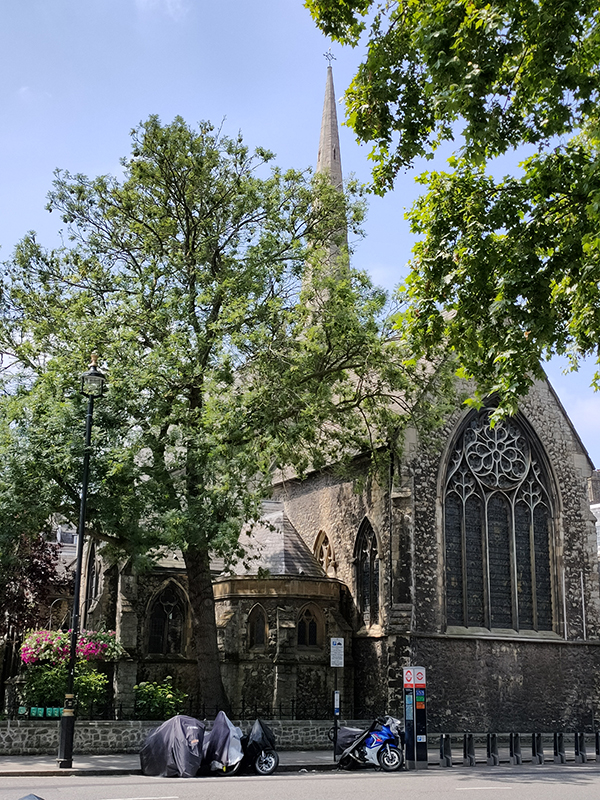
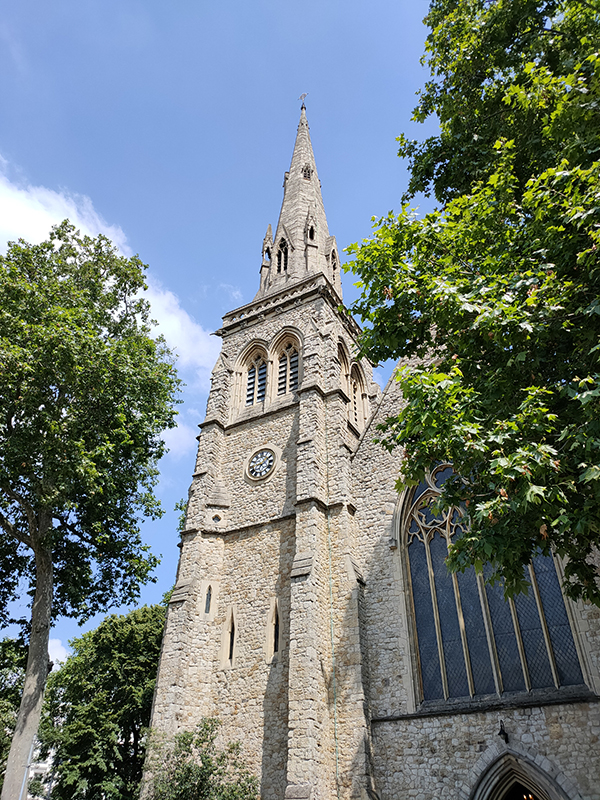
At the southern end of Warwick Square, which we return to next, stands St Gabriel’s Church. St Gabriel’s is a middle-pointed building in decorated Gothic style. It was consecrated in 1853 having been funded by public subscription. The 160ft tower was hung with a peal of eight bells two years later. In 1887 the tower was rebuilt after stonework fell off it, narrowly missing a member of the congregation.
On the other side of the church, on Cambridge Street, is the house (no.114) where the enfant terrible of the Victorian art world, Aubrey Beardsley (1872 – 1898) lived for part of his short life. Beardsley’s six years’ of creative output began at the age of twenty following a stay in Paris. He specialised in black and white illustrations with leanings towards the Art Nouveau style that was in vogue at the time and his work depicted historical events and mythological scenes using grotesque and openly erotic imagery. Probably his most famous drawings were those he produced for Oscar Wilde’s play Salome. With his unusual looks and flamboyant dress sense his public persona did nothing to dampen down the scandalised reaction to his work. In 1966, nearly seventy years after his death from tuberculosis at the age of 25 a private gallery in London was raided by the police for exhibiting copies of his prints and the owner charged under obscenity laws. The originals of those very same prints were contemporaneously being exhibited at the V&A.
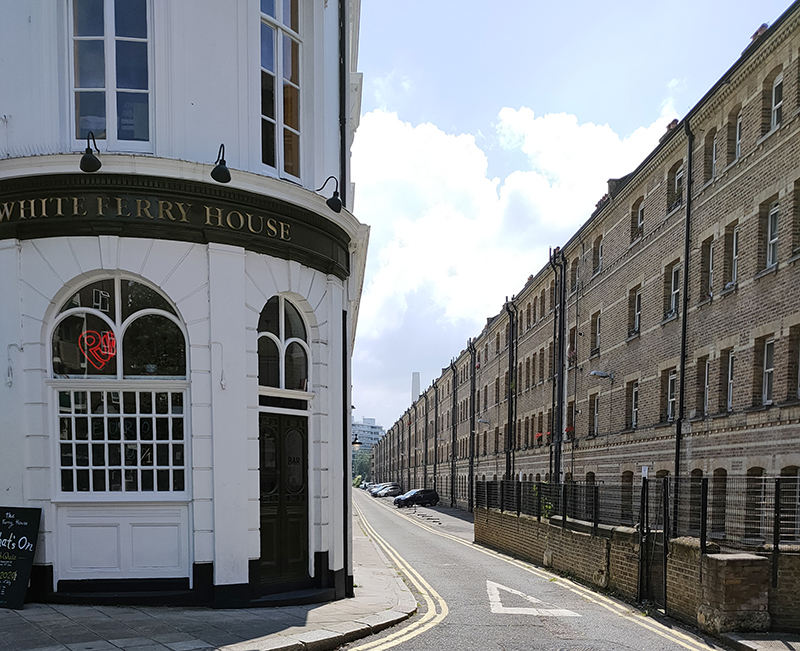
From here repeat visits to Charlwood Street, Alderney Street, Winchester Street and Clarendon Street take us to the western limit of today’s journey and a stop for a quick half at the pub of the day, the White Ferry House on Sutherland Street. This dates back to 1856 and doubled as a hotel when first opened. The original Victorian interior panelling is still in situ which has no doubt contributed to the pub’s Grade II listing.
Next door to the pub is another launderette to add to the collection (in the correctly spelt section) and beyond it lies Peabody Avenue which runs through another of the eponymous trust’s estates.
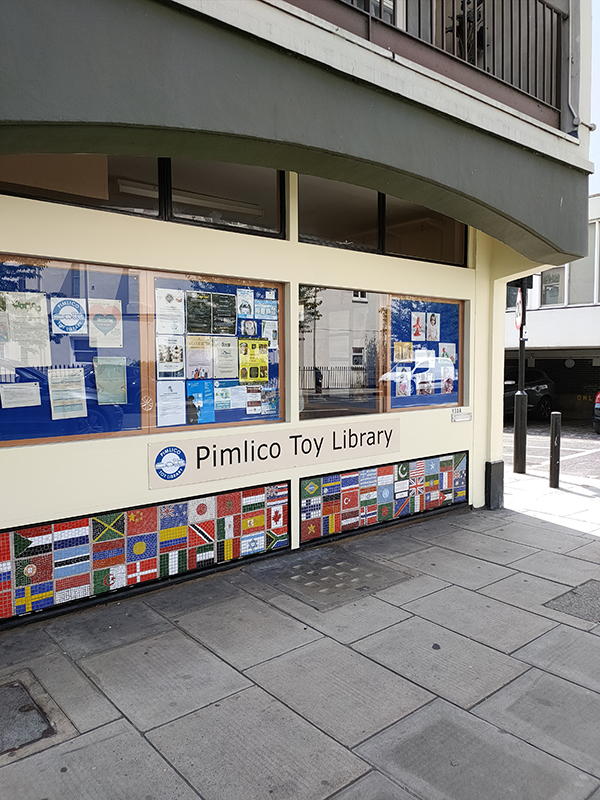
Parallel to Peabody Avenue is Turpentine Lane which, as you can see above, tracks the rear of the Peabody Estate. At the southern end of this we’re in sight of the river on Lupus Street but immediately double back and wend our way around Westmoreland Terrace, Westmoreland Place, Sussex Street, Sutherland Street and Winchester Street. Hopefully by now you’ve got the picture when it comes to the naming of the streets in this part of town. Basically, it’s just Lord Grosvenor namechecking his Ducal chums. Like walking through a cast list of one of Shakespeare’s history plays. Anyway we’re back on Lupus Street now and the area suddenly has quite a different feel – which is actually a refreshing change. Lupus Street is home to the Pimlico Toy Library, a charity set up by Westminster Adult Education services in 1983 to support parents who wanted a safe environment for their children to play. It seems like a good idea so it’s perhaps surprising that other London boroughs don’t appear to have picked up on it.
Lupus Street runs to the north and west of the massive Churchill Gardens Estate which is where we head next. The estate was developed between 1946 and 1962 to a design by the architects Powell and Moya, replacing Victorian terraced houses which had been extensively damaged during the Blitz. Comprising 1,600 homes in 32 blocks, the estate is notable as the only housing project completed under the ambitious Abercrombie Plan to redevelop the capital on more “efficient” lines. A stroll through Glasgow Terrace, Churchill Gardens Road and Paxton Terrace brings us out onto Grosvenor Road and the river. As I enter the Estate an exuberant school jazz-band rendition of “It’s Not Unusual” blasts out from St Gabriel’s Church Hall.
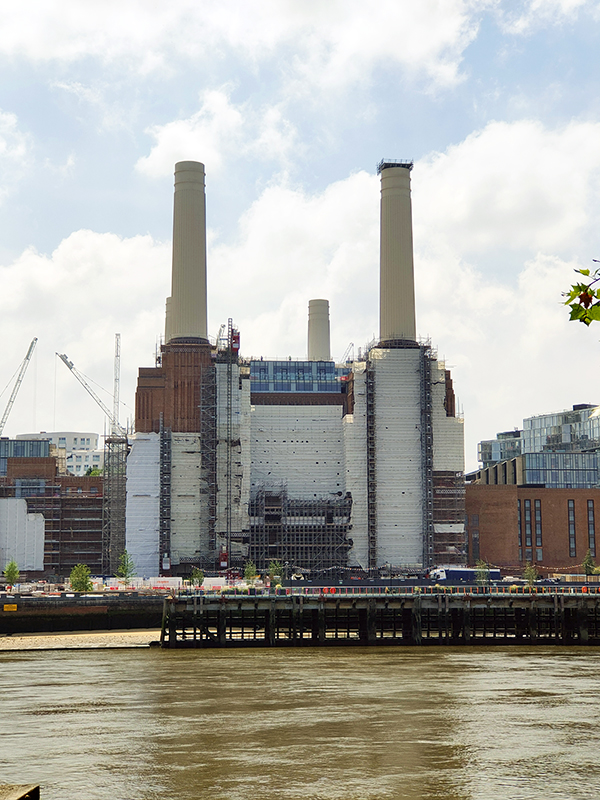
The estate is also notable for its early and rare example of district heating in the UK, the Pimlico District Heating Undertaking. A glass-faced accumulator tower was built to store hot water that would otherwise have been a wasted by-product of Battersea Power Station on the opposite side of the Thames, providing heating and hot water throughout the estate. Churchill Gardens was designated a conservation area in 1990, and in 1998 six blocks (Chaucer House, Coleridge House, Shelley House, Keats House, Gilbert House and Sullivan House) as well as the accumulator tower were Grade II listed. Battersea Power Station is, of course, now in the final stages of a mammoth commercial and residential redevelopment (which no doubt we will get to eventually).
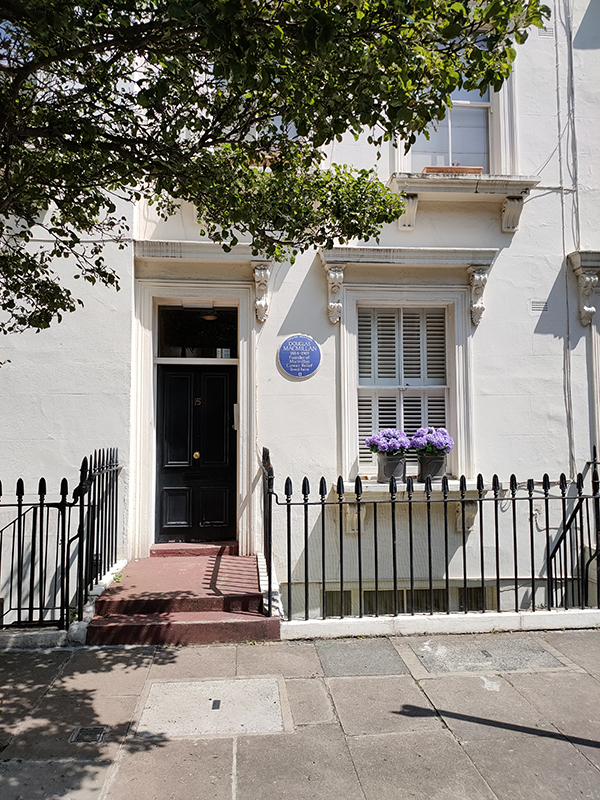
After a jaunt alongside the river we follow Claverton Street and Johnson’s Place back to Lupus Street and find another washeteria to add to the collection (the other section this time). Then a detour into Ranelagh Road uncovers a blue plaque at no.15 in honour of Douglas Macmillan (1884 – 1969). In 1912 Macmillan set up the Society for the Prevention and Relief of Cancer following the death of his father from the disease the year before. It wasn’t until 1930 that the charity, which now bears his name, took on its first full time employee but since then it has grown into one of the largest charities in the UK. Macmillan himself died of cancer at the age of 84.
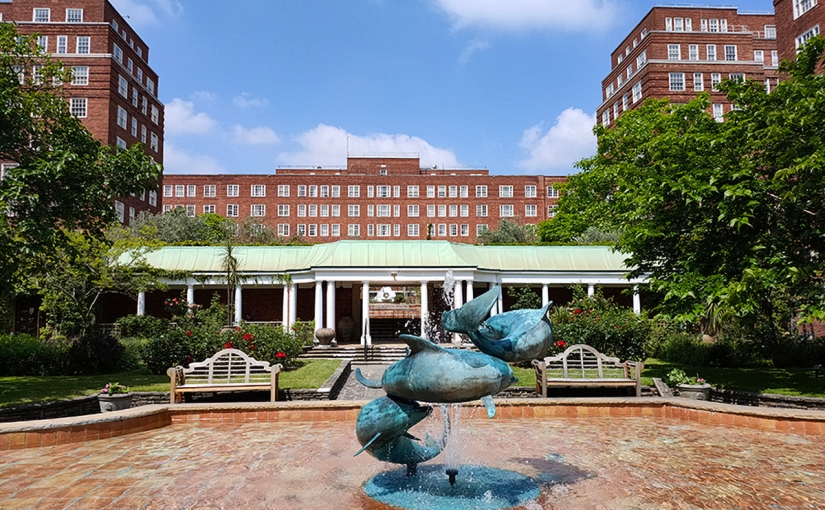
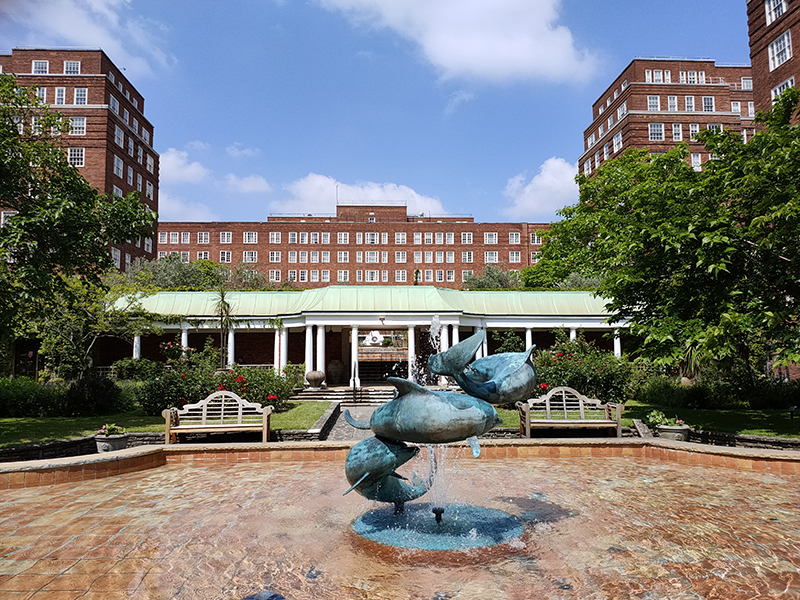
Crossing over into Chichester Street affords access to the northern end of an estate of an entirely different tenor, Dolphin Square. Built between 1935 and 1937, Dolphin Square consists of 13 blocks (or “houses”), each named after a famous navigator or admiral, that together provide 1,310 high-end private flats. After reclamation of the land it was the site of Thomas Cubitt’s works while Pimlico was being developed. Following Cubitt’s death, The Royal Army Clothing Depot was built on the site and stood until 1933 when the leasehold reverted to the Duke of Westminster. The freehold was soon acquired by an American firm but when they ran into difficulties it was sold on to Richard Costain Ltd who engaged architect, S. Gordon Jeeves to draw up plans for housing development. The buildings he designed are neo-Georgian in style with external facings of brick and stone. The original cost of construction was around £2m with 200,000 tonnes of earth moved and 125,000 tons of concrete and 12 million bricks used on those external walls. The 3.5 acres (1.4 ha) of communal gardens were designed by Richard Sudell, president of the Institute of Landscape Architects, and since 2018 have been Grade II listed (unlike the buildings). When it opened the flats varied in size from one-bedroom suites to apartments with five bedrooms, a maid’s room and three bathrooms. Due to its proximity to the Palace of Westminster (and the HQs of MI5 and MI6) the square has, over the years, provided accommodation for many MPS, peers, civil servants and spooks. Harold Wilson, William Hague and David Steel are among the politicians who have lived here; as did Christine Keeler and Mandy Rice-Davies (though not at the same time). Oswald Mosley and his wife Diana Mitford left their apartment here for internment in 1940 during the Second World War. In 2014, the Met opened an inquiry into allegations that some of the flats had been used by a VIP paedophile ring run by a number of prominent MPs, with the case receiving significant media coverage. Within two years it emerged that the accuser, Carl Beech, had fabricated the story and in 2019 Beech was the one convicted (for false allegations).
Reaching the southern end of Dolphin Square we exit out onto Grosvenor Road again and after a left turn begin a circuit of St George’s Square. This is the southernmost and least grand of the garden squares laid out by Thomas Cubitt and the only one whose gardens are open to the public.
At the north end of the square stands St Saviour’s Anglo-Catholic church which, like St Gabriel’s, was designed by Thomas Cundy. It was consecrated in 1864 and, at the time, its 170ft spire was one of the tallest in London. The founder of modern lawn tennis, Walter Clopton Wingfield, was a regular worshipper and the writer Sir Compton Mackenzie was married in the church.
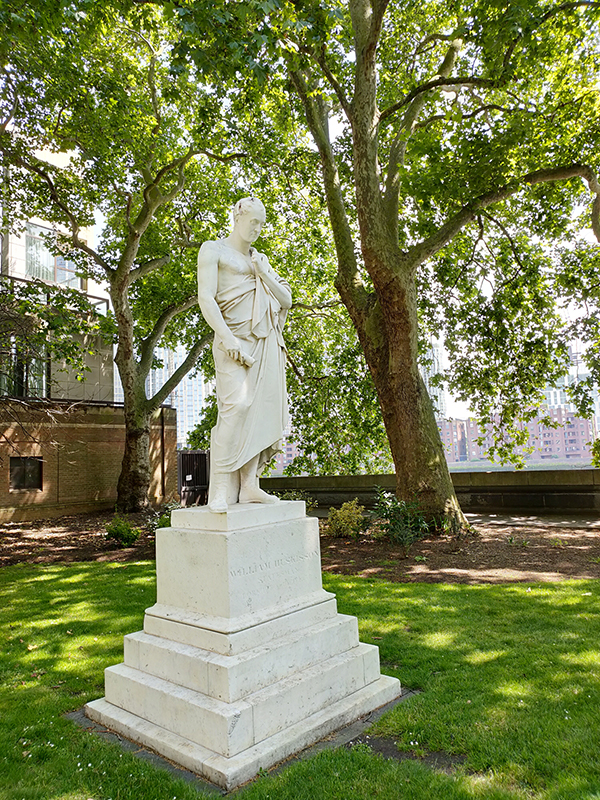
Having completed a circuit of the square we cross over Grosvenor Road to the (small) riverside Pimlico Gardens. Here you’ll find a statue of the early nineteenth century politician William Huskisson (1770 – 1830) who, as we first recorded many moons ago, is now best known for being the first person to be killed in a railway accident, having been run over by Stephenson’s Rocket. The statue was created by John Gibson and was moved here in 1915 having originally been designed for the Royal Exchange. It’s not really clear why Huskisson is wearing a toga other than to make a tenuous connection between the House of Commons and the Roman senate.
To conclude we cross Grosvenor Road for a final time and let St George’s Mews and Aylesford Street take us back to Pimlico Tube Station. I’ll leave you with this – the origin of the name Pimlico is not properly known but H.G. Wells, in his novel The Dream, says that there was a wharf here where ships from America docked and that the word Pimlico came with the trade and was the last word left alive of the Algonquin Indian language (Pamlico). That’ll probably do.